
- Company :
- Brand : CareerMatch
- Homepage : 취업을 하고자 구인구직 사이트에 들어가서 구인공고를 검색하는 사용자를 대상으로 관심있는 구인공고를 인공지능이 매칭해 주고, 해당 구인공고에서 원하는 인재상 및 요구조건에 맞게 자기소개서를 작성하고, 지원까지 대신해 주는 서비스. 구직자에게 월 2만원의 구독료를 받음
1. Service Overview
1.1 Service Definition
CareerMatch is an AI-powered subscription service that transforms how job seekers interact with job listings, create application materials, and manage their application process.
- Service Classification: AI-Powered Recruitment SaaS / Job Application Automation Platform
- Core Functionality: CareerMatch uses artificial intelligence to match users with relevant job postings, automatically generate tailored application materials, and submit applications on behalf of users.
- Establishment Year: 2023 (conceptual)
- Service Description: CareerMatch leverages advanced AI algorithms to analyze job seekers’ skills, experience, and preferences, then identifies and recommends highly relevant job opportunities from various job boards. The platform automatically generates customized cover letters and resumes that align with specific job requirements and employer preferences. It also manages the application submission process, saving users considerable time and effort while increasing their chances of securing interviews.
[swpm_protected for=”4″ custom_msg=’This report is available to Harvest members. Log in to read.‘]
1.2 Value Proposition Analysis
CareerMatch addresses several critical pain points in the job search process while delivering significant time savings and improved application quality for its users.
- Core Value Proposition: CareerMatch eliminates the time-consuming and often frustrating process of searching for relevant job listings, tailoring applications for each position, and managing multiple submissions, while increasing match quality between job seekers and potential employers.
- Primary Target Customers: Active job seekers (particularly recent graduates, professionals in transition, and frequent job changers), career advancement seekers looking for better opportunities, and busy professionals who lack time for comprehensive job searches.
- Differentiation Points: Unlike traditional job boards that merely list opportunities or basic resume builders, CareerMatch offers end-to-end automation of the entire application process, intelligent job matching based on both explicit and implicit user preferences, and AI-generated application materials customized for each specific position.
1.3 Value Proposition Canvas Analysis
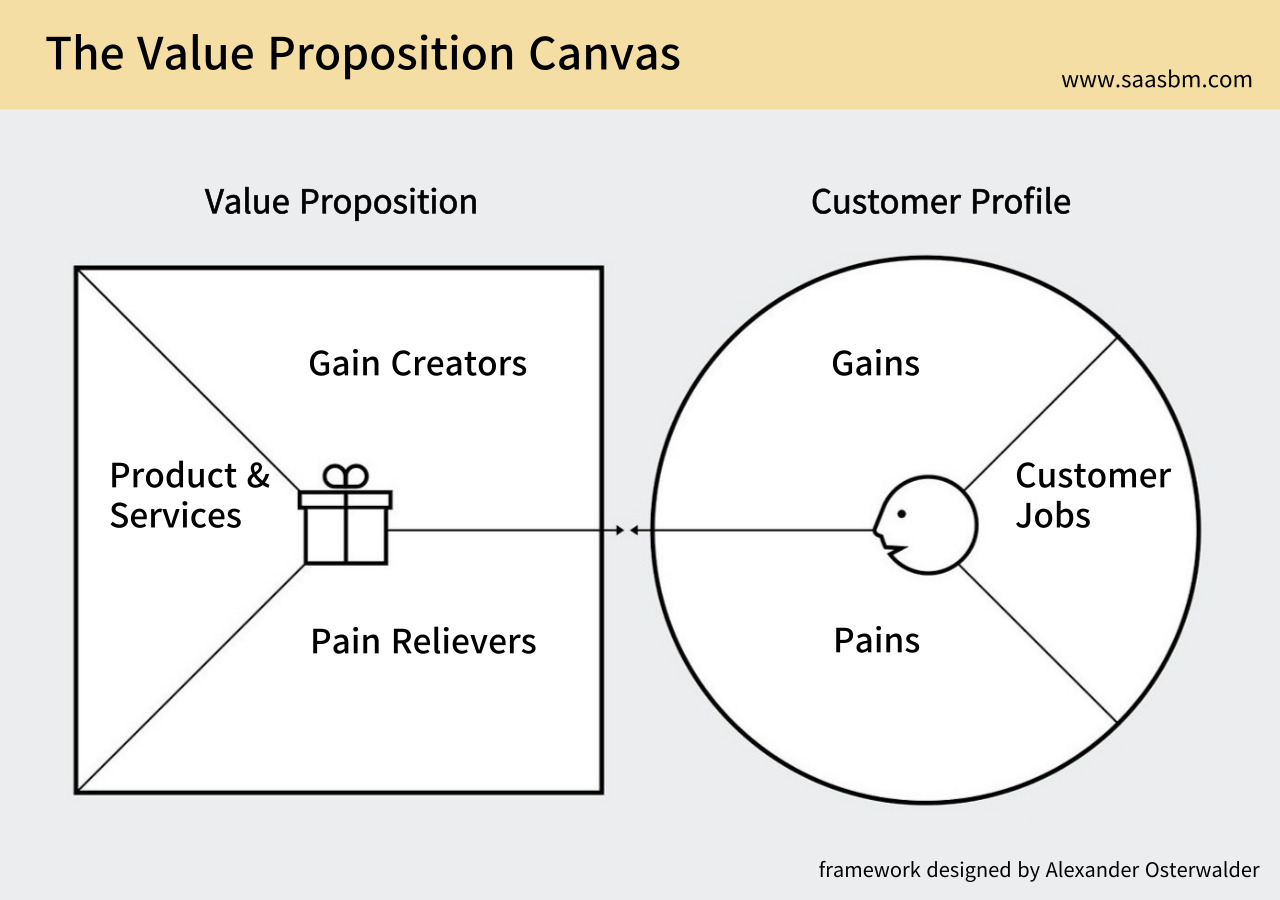
The Value Proposition Canvas systematically analyzes customer needs, difficulties, and expected gains, mapping how CareerMatch’s features connect with these elements.
Customer Jobs
- Finding relevant job opportunities that match skills and career goals
- Creating compelling, tailored resumes and cover letters for each application
- Managing and tracking multiple job applications simultaneously
- Maximizing chances of securing interviews and job offers
Customer Pain Points
- Time-consuming process of searching through numerous job boards
- Difficulty in customizing application materials for each position
- Uncertainty about whether application materials meet employer expectations
- Frustration from lack of responses or feedback from applications
Customer Gains
- Time savings through automation of repetitive tasks
- Higher quality, professionally tailored application materials
- Increased application success rate and interview opportunities
- Reduced stress and improved confidence in job search process
Service Value Mapping
CareerMatch systematically addresses each pain point through its feature set: The AI matching algorithm eliminates hours of manual job searching by automatically identifying relevant opportunities across multiple platforms. The automated resume and cover letter generation solves the customization challenge by analyzing job descriptions and creating tailored materials that emphasize relevant skills and experiences. The application tracking system reduces uncertainty by managing all applications in one place with status updates. By optimizing the entire process, the service increases the likelihood of positive responses, directly addressing the frustration of non-responsive applications.
1.4 Jobs-to-be-Done Analysis
The Jobs-to-be-Done framework analyzes the fundamental reasons why customers “hire” CareerMatch, the contexts in which they do so, and their criteria for success.
Core Job
The primary job users hire CareerMatch to perform combines both functional and emotional dimensions: functionally, to secure relevant job opportunities with minimal time investment; emotionally, to reduce the anxiety and uncertainty of job searching while boosting confidence in application quality. Users essentially hire CareerMatch to transform an overwhelming, time-consuming process into a streamlined, confidence-building experience that produces better results.
Job Context
This job arises during career transitions, periods of unemployment, or when users seek better opportunities while employed. It occurs with high frequency during active job searches (daily or weekly) and carries significant importance as it directly impacts users’ financial stability and career progression. The job becomes particularly critical during competitive job markets, recession periods, or when users face time constraints due to current employment or personal responsibilities.
Success Criteria
Users evaluate CareerMatch’s job performance based on several key metrics: the relevance and quality of job matches (do they align with skills and aspirations?), the perceived quality of generated application materials (do they appear professional and tailored?), time saved compared to manual applications, and ultimately, response rate from employers (interview invitations). Success is measured both quantitatively (number of quality applications submitted, interview rate) and qualitatively (reduced stress, increased confidence).
2. Market Analysis
2.1 Market Positioning
CareerMatch operates at the intersection of several evolving market segments, positioning itself to capitalize on emerging trends in recruitment technology.
- Service Category: AI-Enhanced Job Application Automation / Career Services SaaS
- Market Maturity: Growth phase – The broader recruitment technology market is well-established, but the specific niche of end-to-end AI-powered application automation remains in early growth stages. Current solutions typically address only portions of the application process rather than the comprehensive approach of CareerMatch.
- Market Trend Relevance: CareerMatch aligns with several significant market trends: the growing reliance on AI in recruitment (both for employers and job seekers), increasing demand for personalization in job matching, the rise of automation tools for repetitive tasks, and the shift toward subscription-based digital services that deliver tangible time savings and improved outcomes.
The total addressable market is substantial, with approximately 27 million Americans changing jobs annually pre-pandemic, and this number increasing with recent “Great Resignation” trends. Globally, the online recruitment market is projected to reach $43.4 billion by 2027, with tools for job seekers representing a significant segment.
2.2 Competitive Environment
CareerMatch faces competition from various services that address different aspects of the job search process, though few competitors offer its comprehensive end-to-end approach.
- Key Competitors: LinkedIn Premium, Indeed Premium, Hired, ZipRecruiter, Resume.io, Novoresume
- Competitive Landscape: The market is fragmented, with different players specializing in specific aspects of the job search process: job boards with premium matching features (LinkedIn, Indeed), resume building tools (Resume.io, Novoresume), and recruiter marketplaces (Hired). No single competitor currently offers the fully integrated, AI-driven application automation that CareerMatch proposes. Most competitors focus on either improving job discovery or enhancing application materials, but not automating the entire process.
- Substitutes: Traditional approaches include manual job searching across multiple platforms, hiring professional resume writers, using free templates, working with recruiters/headhunters, and leveraging personal networks. These alternatives typically require more time investment, lack personalization at scale, or come with significantly higher costs (professional services).
The competitive landscape is evolving rapidly as AI capabilities advance, with major players increasingly incorporating machine learning into their offerings, though most still require significant user involvement in the application process.
2.3 Competitive Positioning Analysis
This analysis maps CareerMatch’s relative position against key competitors based on critical differentiating factors.
Competitive Positioning Map
The positioning map reveals how CareerMatch occupies a unique space in the market landscape by evaluating competitors across two critical dimensions that matter most to users.
- X-axis: Level of Process Automation (low to high) – measuring how much manual work is eliminated for the user
- Y-axis: Personalization Depth (generic to highly tailored) – measuring how customized the service output is for specific job applications
Positioning Analysis
CareerMatch occupies the highly desirable upper-right quadrant, combining high automation with deep personalization.
- LinkedIn Premium: Positioned with medium personalization (offers job recommendations and insights) but low-to-medium automation (user still needs to search, create materials, and apply manually).
- Resume.io/Novoresume: Offers medium personalization for resume creation but low automation across the full application process.
- Indeed Premium: Similar to LinkedIn but with slightly lower personalization depth in its recommendations and fewer premium insights.
- ZipRecruiter: Provides medium automation through its 1-click apply feature but offers limited personalization of application materials.
- CareerMatch: Uniquely positioned with high automation (handling matching, document creation, and submission) combined with high personalization (each application is specifically tailored to the job requirements). This positioning addresses the two most significant pain points for job seekers: time investment and application quality.
3. Business Model Analysis
3.1 Revenue Model
CareerMatch employs a subscription-based revenue model with clear pricing tiers to generate predictable recurring revenue.
- Revenue Structure: Subscription-based model with a fixed monthly fee of $20, positioning the service as affordable yet valuable for active job seekers.
- Pricing Strategy: CareerMatch adopts a straightforward pricing approach with a single core tier at $20/month, deliberately priced below premium tiers of major job platforms (like LinkedIn Premium at $29.99-$59.99/month) to appear as an accessible alternative. The strategy focuses on volume and retention rather than premium pricing, acknowledging the potentially temporary nature of job seeking.
- Free Offering Scope: While maintaining the core $20 subscription, CareerMatch could implement a limited freemium model allowing users to access basic job matching and a limited number of auto-generated applications (e.g., 2-3 per month) to demonstrate value before committing to a subscription. The free tier would serve primarily as a customer acquisition funnel.
The subscription approach aligns with user behavior patterns in job seeking, which typically involves a concentrated period of activity (3-6 months) rather than continuous long-term usage. This creates a natural customer lifecycle with opportunities for reactivation during future job transitions.
3.2 Customer Acquisition Strategy
CareerMatch’s customer acquisition strategy leverages multiple digital channels with a focus on demonstrating immediate value to job seekers.
- Key Acquisition Channels: Search engine marketing targeting high-intent keywords related to job searching and resume building; content marketing addressing job search pain points; strategic partnerships with career coaching services, educational institutions, and professional associations; and targeted social media campaigns on platforms where job seekers are active (particularly LinkedIn, Twitter, and Reddit communities focused on career advancement).
- Sales Model: Primarily self-service, allowing users to sign up and begin using the platform immediately without sales intervention. This approach supports scalability while keeping customer acquisition costs manageable. For potential enterprise opportunities (e.g., outplacement services for companies during layoffs), a limited inside sales function could be developed.
- User Onboarding: CareerMatch employs a streamlined, value-first onboarding flow designed to deliver immediate results. New users upload their existing resume or complete a quick skills/experience profile, select industry and role preferences, and receive initial job matches within minutes. The platform then guides users through the AI-driven customization process, allowing them to review and approve generated application materials before submission.
The acquisition strategy emphasizes rapid time-to-value, allowing users to see relevant job matches and sample generated materials early in the experience to demonstrate the platform’s capabilities and encourage subscription conversion.
3.3 SaaS Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas framework provides a systematic analysis of CareerMatch’s complete business structure.
Value Proposition
End-to-end automation of job search and application process, delivering personalized job matches and professionally tailored application materials at scale.
Customer Segments
Primary: Active job seekers, recent graduates, professionals in career transition. Secondary: Employed professionals seeking better opportunities, freelancers looking for new projects/clients.
Channels
Direct web platform, mobile application, email notifications, integration with major job boards (via APIs), potential white-label solutions for career services.
Customer Relationships
Primarily automated self-service with personalized AI interactions, supplemented by email support, usage tips, and success metrics dashboards.
Revenue Streams
Monthly subscription fees ($20/month), potential premium tiers for enhanced features, possible enterprise partnerships (outplacement services).
Key Resources
AI matching algorithms, natural language generation technology, database of job listings (aggregated), skilled AI/ML development team, user data and feedback loops.
Key Activities
Algorithm development/refinement, job listing aggregation and processing, automated content generation, platform maintenance, user experience optimization, marketing and user acquisition.
Key Partnerships
Job boards and career platforms (for API access), HR technology providers, resume parsing services, payment processors, career coaching services, educational institutions.
Cost Structure
AI/ML talent, computational resources, API access fees to job platforms, marketing and user acquisition, infrastructure and development costs.
Business Model Analysis
CareerMatch’s business model shows several strengths: The subscription approach creates predictable recurring revenue while keeping the pricing accessible to job seekers. The self-service nature allows for scalability without proportionally increasing operational costs. The value proposition addresses clear, significant pain points with measurable benefits (time savings, improved response rates).
Key challenges include: Potentially high customer churn due to the temporary nature of job searching, requiring continuous acquisition efforts; competition from well-funded job platforms that could develop similar capabilities; and dependency on integration with job listing sources that could restrict access. The model’s sustainability depends on maintaining a healthy LTV:CAC ratio by extending average subscription length and optimizing acquisition costs.
4. Product Analysis
4.1 Core Functionality Analysis
CareerMatch delivers value through several interconnected functional components that work together to automate and enhance the job application process.
- Key Functional Categories: AI-powered job matching and recommendation engine; advanced resume and cover letter generation system; application tracking and management dashboard; automated submission integration; skills and experience profile management.
- Key Differentiating Features: Contextual job matching that understands both explicit and implicit user preferences; hyper-personalized application document generation that aligns precisely with specific job requirements; end-to-end automation that handles the entire process from discovery to submission.
- Functional Completeness: CareerMatch offers comprehensive coverage of the job application process compared to competitors that typically focus on specific segments. The platform’s automated content generation capabilities exceed most resume builders in personalization depth, while its matching algorithm incorporates more contextual factors than standard job boards.
The platform’s AI engine analyzes key patterns in successful job applications across industries and roles, applying these insights to user documents. The system continuously improves through machine learning, incorporating feedback from application outcomes to refine both matching and document generation. While competitive job boards offer basic filtering and saved searches, CareerMatch’s proactive matching goes beyond by identifying opportunities users might miss and presenting them with clear justification for why each opportunity matches their profile.
4.2 User Experience
CareerMatch’s user experience focuses on simplicity, transparency, and user control despite the sophisticated technology working behind the scenes.
- UI/UX Characteristics: Clean, distraction-free interface that emphasizes job matches and application status; dashboard-centered design that provides clear visibility into the user’s job search activity; transparent AI processes that allow users to understand why matches were made and how documents were customized.
- User Journey: The core user flow begins with profile creation or resume upload, followed by preference setting. Users then receive personalized job matches, review AI-generated application materials with the ability to edit before submission, and track application status through a unified dashboard. The platform sends notifications about new matches and application updates.
- Accessibility and Ease of Use: CareerMatch prioritizes accessibility through intuitive workflows that require minimal training. The complexity of the underlying AI is abstracted through simple interfaces, while still allowing users control over final submissions. The service maintains the appropriate balance between automation and user agency, especially important for sensitive documents like resumes and cover letters.
A key design principle is maintaining transparency about the automated processes – users can see which aspects of their profile matched specific job requirements and how these elements were incorporated into application materials. This transparency builds trust in the AI’s decisions while still providing users the final approval before submission.
4.3 Feature-Value Mapping Analysis
This analysis maps how CareerMatch’s key features deliver specific customer value and evaluates their differentiation level compared to competitors.
| Core Feature | Customer Value | Differentiation Level |
|---|---|---|
| AI Job Matching Engine | Saves hours of search time by automatically identifying relevant opportunities; reduces chances of missing suitable positions; prioritizes jobs with higher match potential | Medium-High |
| Personalized Document Generation | Eliminates the need to customize each application manually; ensures application materials highlight the most relevant qualifications for each position; maintains professional quality across all documents | High |
| One-Click Application Submission | Removes friction from the application process; allows for higher volume of quality applications; eliminates repetitive form-filling | Medium |
| Unified Application Tracking | Provides clear visibility into application status across multiple positions and platforms; enables better follow-up management; reduces anxiety about application status | Medium |
| Integrated Feedback Loop | Continuously improves match quality and document generation based on application outcomes; adapts to changing job market and user preferences | High |
Mapping Analysis
CareerMatch’s most significant competitive advantage lies in the personalized document generation system, which delivers highly customized materials with minimal user effort – a feature with both high value to users and strong differentiation from existing solutions. While one-click submission and tracking features exist in some form across other platforms, CareerMatch’s integration of these features into a comprehensive workflow creates multiplicative value.
The service’s most innovative aspect is the integrated feedback loop that leverages application outcomes to continuously improve both the matching algorithms and document generation. This creates a virtuous cycle where the service becomes more effective as its user base grows. Potential improvement opportunities include more advanced interview preparation features, negotiation guidance for offer stages, and deeper integration with professional networking platforms to leverage connections at target companies.
5. Growth Strategy Analysis
5.1 Current Growth State
CareerMatch currently exists in a conceptual stage poised for market entry, with clear growth opportunities based on market conditions and technological capabilities.
- Growth Stage: Pre-launch/Early introduction stage – The service concept has been developed but has not yet been fully introduced to the market. This positions CareerMatch at the beginning of the product lifecycle, with significant growth potential ahead if execution is successful.
- Expansion Direction: Initial focus should be on product-market fit validation with a core offering targeting active job seekers in knowledge worker categories where AI matching and document generation can deliver the strongest results (technology, marketing, business operations, etc.). Both product feature expansion and market segment expansion present viable growth paths once the core service proves successful.
- Growth Drivers: Primary growth will be driven by several factors: increasing adoption of AI-powered tools across industries; continued evolution of the gig economy and job mobility; rising expectations for personalization in digital services; and growing willingness to pay subscription fees for tools that deliver tangible time savings and improved outcomes.
The current environment is particularly favorable for CareerMatch’s growth due to several market factors: the ongoing “Great Resignation” and job reshuffling has increased the pool of active job seekers; remote work trends have expanded the geographic scope of job searches; and economic uncertainty has heightened competition for desirable positions, increasing the value of tools that provide an edge in applications.
The growth trajectory will likely follow an initial period of rapid user acquisition as early adopters experience and share results, followed by more mainstream adoption as the service builds credibility and demonstrates consistent value delivery.
5.2 Expansion Opportunities
CareerMatch can pursue multiple expansion avenues to increase market share, revenue, and user value over time.
- Product Expansion Opportunities: Career development advisory features using predictive analytics to suggest skill development paths; interview preparation tools including AI-simulated interviews with feedback; salary negotiation assistance using market data; expanded profile building with portfolio integration for creative roles; and enterprise tools for internal mobility within large organizations.
- Market Expansion Opportunities: Geographic expansion beyond English-speaking markets; industry-specific versions targeting sectors with unique application requirements (healthcare, legal, education); experience-level targeting from entry-level to executive positions; and strategic partnerships with educational institutions for recent graduates.
- Revenue Expansion Opportunities: Premium tiers with advanced features (priority matching, unlimited applications); add-on services such as professional review of AI-generated materials; affiliate partnerships with skills development platforms; and B2B offerings for outplacement services, recruitment agencies, and career services departments.
A particularly promising expansion opportunity lies in creating industry-specific versions of the platform that incorporate deep knowledge of particular sectors. For example, a healthcare-focused version could understand medical credentialing requirements, while a technology-focused version could better match technical skills to specific development environments mentioned in job listings.
The subscription model also creates opportunities for expansion into career development beyond the active job search phase, potentially extending the customer lifecycle from temporary use during job transitions to ongoing career management support that retains users between job searches.
5.3 SaaS Expansion Matrix
The SaaS Expansion Matrix systematically analyzes CareerMatch’s growth pathways and prioritizes the most promising directions.
Vertical Expansion (Vertical Expansion)
Definition: Delivering deeper value to the same customer segment
Potential: High
Strategy: Expand the service offering to cover more aspects of the job search and career development process. This includes adding interview preparation tools, salary negotiation assistance, professional networking features, and long-term career pathing. These additions would extend the user lifecycle and increase the value derived from each customer relationship.
Horizontal Expansion (Horizontal Expansion)
Definition: Expanding to similar customer segments
Potential: Medium
Strategy: Adapt the core platform to serve adjacent user groups with similar needs but different contexts. This includes creating specialized versions for specific industries (healthcare, technology, finance) or experience levels (entry-level, mid-career, executive). Each adaptation would require domain-specific knowledge integration into the AI systems but would leverage the same core technology.
New Market Expansion (New Market Expansion)
Definition: Expanding to new customer segments
Potential: Medium-Low
Strategy: Develop entirely new offerings targeting different stakeholders in the employment ecosystem. This could include tools for employers to better evaluate applications, solutions for career counselors and coaches to support their clients, or platforms for educational institutions to help students transition to the workforce. These would require significant adaptation of the core technology and new go-to-market approaches.
Expansion Priorities
Based on potential impact, resource requirements, and alignment with core capabilities, the following expansion priorities emerge:
- Vertical Expansion – Adding interview preparation and salary negotiation tools to create a comprehensive job search solution represents the highest-priority expansion direction. This leverages existing user relationships, extends lifetime value, and requires reasonable development investment while maintaining focus on the primary user segment.
- Horizontal Expansion: Industry Specialization – Creating industry-specific versions for high-volume, high-complexity sectors like technology and healthcare would capture higher-value users with more specific needs, potentially enabling premium pricing.
- Horizontal Expansion: Geographic/Language – Expanding to additional markets through localization would increase the addressable market while leveraging the existing technology base, though it would require adapting to different job market dynamics and cultural expectations.
6. SaaS Success Factors Analysis
6.1 Product-Market Fit
This analysis evaluates how well CareerMatch aligns with market needs across multiple dimensions.
- Problem-Solution Fit: CareerMatch addresses high-importance problems (time-consuming job searches, difficulty creating tailored applications, uncertainty about application quality) with an effective solution. The job application process represents significant time investment for professionals, with studies showing average job seekers spend 11 hours per week on search activities. The service’s automation approach directly addresses this time burden while potentially improving outcomes.
- Target Market Fit: The selected target market of active job seekers is appropriate for several reasons: it’s a large and continually replenishing market (with approximately 20-30% of professionals actively job searching at any given time); it has demonstrated willingness to pay for advantage-conferring tools; and it experiences acute pain points that the service addresses. The $20 monthly price point is also well-calibrated to this market’s willingness to pay.
- Market Timing: The timing appears favorable due to several converging factors: widespread acceptance of AI-driven tools in professional contexts; increasing job mobility creating more active job seekers; growing sophistication of natural language generation technology enabling higher quality outputs; and heightened competition for desirable positions increasing the value of application optimization.
CareerMatch demonstrates strong potential for product-market fit based on the significance of the problems it solves and current market conditions. The service concept aligns with demonstrable user needs rather than creating a solution in search of a problem. A critical success factor will be ensuring the AI-generated materials consistently meet or exceed the quality users could create themselves, as this represents the core value proposition.
The primary risk to product-market fit lies in execution quality – if the AI matching proves inaccurate or document generation appears generic, users will quickly abandon the service. Continuous improvement of these core capabilities must remain the central focus.
6.2 SaaS Key Metrics Analysis
This analysis examines the key operational metrics likely to determine CareerMatch’s success as a SaaS business.
- Customer Acquisition Efficiency: CareerMatch’s acquisition approach should achieve reasonable efficiency through targeted digital marketing channels and a self-service model. By focusing on high-intent keywords and platforms where job seekers already congregate, the service can reach prospects at the moment of need. The clear, tangible value proposition should enable effective messaging and conversion. The self-service model eliminates sales costs that typically drive up CAC in many SaaS businesses.
- Customer Retention Factors: The service faces inherent stickiness challenges due to the typically temporary nature of job searching. However, several factors can enhance retention: the continuous delivery of new, relevant job matches creates ongoing value; the learning effect where the system improves with user feedback increases switching costs; and the unified application tracking keeps users engaged throughout the process. Success metrics visibility (showing users how many applications submitted, response rates, etc.) can also drive continued usage.
- Revenue Expansion Potential: While the core subscription provides limited immediate upsell opportunity, CareerMatch has several paths to expand revenue per user: premium tiers with advanced features or unlimited applications; add-on services like professional review or coaching; and expanded offerings covering additional aspects of career development. A key strategy should be extending the user relationship beyond active job searching into ongoing career management.
The service’s unit economics will be heavily influenced by average subscription duration. If users subscribe for an average of 3-4 months during a job search cycle, customer lifetime value can remain healthy despite the relatively low monthly price point. Reactivation strategies to bring users back during future job transitions will be crucial for long-term economics.
A key metric to track will be the “success rate” – defined as users securing interviews and ultimately jobs through the platform – as this directly correlates with perceived value and word-of-mouth potential. Developing mechanisms to attribute positive outcomes to the service will strengthen retention and referrals.
6.3 SaaS Metrics Evaluation
This evaluation estimates and assesses key SaaS business metrics to analyze CareerMatch’s economic viability.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Estimate: Medium
Rationale: CareerMatch would likely experience moderate customer acquisition costs due to the competitive nature of job-related keywords in digital advertising. However, the self-service model, clear value proposition, and potential for organic growth through user referrals should keep CAC from reaching the high levels seen in enterprise SaaS. Estimated CAC would be in the $40-70 range, requiring 2-3.5 months of subscription to recover.
Industry Comparison: This CAC would be lower than enterprise HR tech solutions but higher than typical B2C subscription services, positioning it appropriately for a prosumer SaaS offering targeting individuals with professional needs.
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
Estimate: Medium
Rationale: With a $20 monthly subscription and estimated average retention of 3-5 months during an active job search period, baseline LTV would be $60-100. This could increase with effective reactivation campaigns bringing users back for future job searches (potentially every 2-3 years) and through the addition of premium features or services. The relatively low price point is offset by the potential for scale and limited per-user costs after acquisition.
Industry Comparison: This LTV range falls below many SaaS businesses but remains viable given the potential for high volume and the lower servicing costs of a largely automated platform.
Churn Rate
Estimate: High (Monthly basis) / Medium (Annual basis)
Rationale: Monthly churn would naturally be high due to the project-based nature of job searching, with many users canceling after securing employment. Monthly churn rates of 20-30% would be expected. However, from an annual perspective, reactivation of previous users would offset this somewhat, resulting in a more moderate effective churn rate. The service should be designed with this usage pattern in mind, making reactivation seamless.
Industry Comparison: The higher churn rate compared to typical SaaS benchmarks (5-7% monthly) reflects the specific use case rather than a product deficiency, though strategies to extend usage beyond active job searching would improve this metric.
LTV:CAC Ratio
Estimate: 1.5:1 to 2:1 initially, with potential to improve to 3:1
Economic Analysis: The initial LTV:CAC ratio suggests marginal economic viability at launch, with significant improvement potential as the service refines its acquisition channels, enhances retention, and develops additional revenue streams. Break-even would occur after 2-3 months of user subscription, which aligns with expected usage patterns.
Improvement Approaches: Key strategies to improve this ratio include: reducing CAC through referral programs and organic growth channels; extending average subscription length through broader career management features; increasing LTV through premium offerings and add-on services; and implementing effective reactivation campaigns to bring past users back during new job searches.
7. Risk and Opportunity Analysis
7.1 Key Risks
CareerMatch faces several significant risk factors that could impact its business trajectory and long-term viability.
- Market Risks: Fluctuations in job market conditions directly impact CareerMatch’s value proposition. During economic downturns with fewer job openings, users may perceive less value in the service. Additionally, regional job market variations could create uneven user experiences, as the service may be more effective in markets with higher job density. Labor market policy changes, including potential regulation of AI in hiring processes, also pose significant uncertainty.
- Competitive Risks: The job search market has entrenched players with substantial resources. LinkedIn, Indeed, and Google Jobs could integrate similar AI capabilities, leveraging their existing massive user bases and data advantages. Low barriers to entry for AI-powered resume services also increase the risk of competitive pressure from nimble startups. Large language model providers might also develop specialized solutions targeting this specific vertical.
- Business Model Risks: The $20 monthly subscription may face resistance in a market accustomed to free job boards. Customer acquisition costs could be high relative to the subscription value, especially if users subscribe only during active job searches rather than maintaining long-term subscriptions. The service also faces potential ethical and legal concerns regarding automated application submissions which some employers might reject or flag.
The most critical risk is likely the integration of similar AI capabilities by established job platforms. These incumbents possess advantages in data scale and existing user relationships that would be difficult for CareerMatch to overcome. The business model also faces uncertainty around user retention, as natural usage patterns may lead to high churn rates once users secure employment. This creates a continual need for new customer acquisition, potentially driving up marketing costs relative to lifetime value.
7.2 Growth Opportunities
Despite the risks, CareerMatch has several compelling growth opportunities that can be leveraged across different timeframes.
- Short-term Opportunities: Integration with major job boards through APIs could expand the service’s reach without requiring users to change their existing job search behaviors. Partnerships with universities and career centers could provide institutional adoption paths and credibility. Implementing a freemium model with basic features available free and premium features for subscribers could lower acquisition barriers while improving conversion.
- Medium to Long-term Opportunities: Expansion into adjacent services like interview preparation, salary negotiation coaching, and career path planning would increase user lifetime value. Enterprise offerings for HR departments and recruiters could open B2B revenue streams by reversing the model to help employers find candidates. International expansion targeting markets with high educated unemployment or workforce mobility would increase the total addressable market.
- Differentiation Opportunities: Developing industry-specific optimization for high-demand sectors like healthcare, technology, or skilled trades would create defensible niches. Incorporating psychometric assessments and career fit analysis could provide users with deeper insights beyond job matching. Building a community platform for peer support and networking would add social value that pure AI solutions cannot replicate.
These opportunities can be strategically sequenced to build competitive advantages. The most immediate priority should be integration with existing job platforms to reduce friction in the user experience. This foundation would support subsequent expansions into complementary services that increase stickiness and extend the customer lifecycle beyond the job application phase. The medium-term focus on industry specialization would make the service progressively more valuable to specific professional segments, creating word-of-mouth referral engines within professional communities. The B2B pivot represents perhaps the most transformative opportunity, potentially shifting the revenue model toward higher-value enterprise subscriptions while maintaining the consumer offering as a user acquisition channel.
7.3 SWOT Analysis
A systematic SWOT analysis provides a framework for understanding CareerMatch’s internal capabilities and external context.
Strengths
- End-to-end automation of the job application process, saving users significant time
- AI-powered personalization that tailors applications to specific job requirements
- Simple, predictable subscription pricing model
- Technology-first approach with lower overhead than traditional recruiting services
Weaknesses
- Limited differentiation from emerging AI resume tools
- Dependence on third-party job listing data
- Lack of human touch in a process that traditionally values personal connection
- Uncertain efficacy metrics compared to traditional application methods
Opportunities
- Growing acceptance of AI tools in professional services
- Increasing job mobility creating larger pools of active job seekers
- Potential for data network effects as user base grows
- Expansion into career development and professional growth services
Threats
- Employers implementing systems to detect auto-generated applications
- Larger platforms integrating similar AI capabilities
- Regulatory concerns around data privacy and automated submissions
- Economic downturns reducing job postings and hiring activity
SWOT-Based Strategic Directions
- SO Strategy: Leverage AI personalization strengths to capitalize on market acceptance of AI tools by expanding into adjacent professional services, creating an ecosystem of career advancement tools.
- WO Strategy: Address the lack of human touch by incorporating community features and peer networking that complement the AI capabilities while taking advantage of increasing job mobility trends.
- ST Strategy: Counter platform competition by developing proprietary effectiveness metrics and success stories that demonstrate superior outcomes compared to both manual applications and competitor AI tools.
- WT Strategy: Mitigate both the commodity risk and employer resistance by developing transparent AI that explains its recommendations and provides users with learning opportunities, positioning the service as an educational tool as well as an application assistant.
8. Conclusions and Insights
8.1 Comprehensive Assessment
CareerMatch represents an innovative attempt to streamline the job application process through AI automation, with several notable aspects of its business model and market position.
- Business Model Sustainability: The subscription-based revenue model provides predictable income, but faces challenges in customer retention due to the inherently episodic nature of job hunting. While the $20 monthly price point is accessible, the lifetime value of customers may be limited by natural usage patterns. To achieve sustainability, CareerMatch must either significantly scale its user base or develop additional services that extend customer lifecycles beyond the job search phase.
- Market Competitiveness: CareerMatch occupies an emerging niche between traditional job boards and premium career services. Its automated approach differentiates it from human-centric services like professional resume writers, while offering more personalization than generic job boards. However, this position is vulnerable to incursion from both directions – established platforms adding AI capabilities and AI assistants expanding into specialized verticals.
- Growth Potential: The service has substantial room for expansion, both within its core functionality and into adjacent services. The global job search market remains massive, with millions of professionals changing roles annually. Opportunities for international expansion, industry specialization, and B2B services provide multiple potential growth vectors if execution is strong.
The fundamental assessment suggests CareerMatch has identified a genuine pain point in the job application process, but faces significant execution challenges. Success will depend on quickly establishing value metrics that demonstrate efficacy compared to both manual applications and competitor services. The business model requires careful balancing of customer acquisition costs against lifetime value, potentially requiring adjustments to the pricing structure or service offerings to optimize economics. While initial differentiation exists in the end-to-end automation approach, the company must continuously innovate to maintain this advantage as larger competitors respond. The most promising path forward combines horizontal expansion into adjacent career services with vertical specialization in high-value professional niches, creating multiple revenue streams while building network effects through growing user data.
8.2 Key Insights
Our analysis of CareerMatch reveals several critical insights that define both its potential and challenges.
Key Strengths
- End-to-end automation creates significant time savings for users, addressing a fundamental friction point in the job application process that competitors have typically addressed only in fragments.
- The AI-powered personalization can potentially deliver higher-quality applications than generic templates, potentially improving conversion rates to interviews.
- The subscription model aligns with modern SaaS business approaches, providing predictable revenue streams and straightforward scaling with user growth.
Key Challenges
- Demonstrating measurable improvements in job application success rates will be critical for word-of-mouth growth and retention, yet these metrics are difficult to isolate from other variables in the hiring process.
- Navigating employer resistance to automated applications may require building transparency features and employer education initiatives to prevent systematic rejection of AI-generated content.
- Customer retention will be inherently challenging due to the episodic nature of job searching, creating a perpetual need for new user acquisition unless service scope expands significantly.
Core Differentiation Elements
CareerMatch’s most powerful differentiation is its comprehensive approach to what has traditionally been a fragmented process. While numerous tools exist for resume building, job matching, or application tracking, CareerMatch creates value through the integration of these elements into a seamless workflow. This integration reduces cognitive load on users and eliminates transition points where job seekers typically abandon their search efforts. The potential for data network effects represents another key differentiator – as the system processes more successful applications, it can refine its understanding of effective application strategies across different industries and roles, creating a virtuous cycle of improvement that would be difficult for new entrants to replicate without similar scale.
8.3 SaaS Scorecard
A quantitative assessment of CareerMatch across key success factors provides perspective on its overall competitive position.
| Evaluation Criteria | Score (1-5) | Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Product Capability | 4 | The core functionality addresses a clear market need with sophisticated AI technology, though the automated application submission may face practical limitations with some employers. |
| Market Fit | 4 | Strong alignment with active job seekers’ needs, particularly for early and mid-career professionals facing competitive application processes. The value proposition resonates most with those applying to multiple positions. |
| Competitive Positioning | 3 | Occupies a distinctive position currently, but faces threats from both established job platforms and AI assistants. Moderate barriers to entry could lead to increased competition. |
| Business Model | 3 | Subscription model is appropriate, but may face challenges with customer retention and lifetime value. The price point balances accessibility with revenue potential. |
| Growth Potential | 4 | Multiple viable expansion paths across additional services, market segments, and geographic regions. Potential for data-driven network effects as user base grows. |
| Total Score | 18/25 | Good – Shows promise with some areas needing refinement |
With a total score of 18/25, CareerMatch demonstrates strong potential as a SaaS business. The service scores highest in product capability and market fit, indicating a solid foundation addressing genuine user needs with effective technology. Its growth potential also scores well, reflecting multiple viable expansion paths. The moderate scores in competitive positioning and business model highlight areas requiring strategic attention. To improve its position, CareerMatch should focus on establishing defensible competitive advantages through data network effects and integration with existing workflows, while optimizing its business model to address the retention challenges inherent in job search services. Overall, CareerMatch represents a promising venture in the evolving landscape of AI-powered professional services, with sufficient strengths to warrant further development and investment, provided the identified challenges are systematically addressed.
9. Reference Sites
9.1 Analyzed Service
CareerMatch’s official website and key related pages.
- Official Website: https://www.careermatch.ai – An AI-powered platform that automates job searching, application personalization, and submission for job seekers through a monthly subscription model.
9.2 Competing/Similar Services
Major services competing with or similar to CareerMatch in the automated job application space.
- LinkedIn Premium: https://premium.linkedin.com – Provides job application insights, candidate comparison, and direct messaging to recruiters, though lacks automated application customization.
- Indeed: https://www.indeed.com – Largest job board globally with Quick Apply features, but offers limited personalization of applications for specific positions.
- Jobscan: https://www.jobscan.co – Focuses on resume optimization against ATS systems but doesn’t handle the application submission process.
- Hugging Face: https://huggingface.co/resume-builder – Offers AI-powered resume building tools with growing sophistication in matching job descriptions.
9.3 Reference Resources
Resources that help with building or understanding similar SaaS businesses.
- OpenAI API: https://openai.com/api/ – Provides the AI capabilities necessary for resume customization and job description analysis.
- AngelList Talent: https://angel.co/talent – Offers job board API integration possibilities for startups in the recruiting space.
- Recurly: https://recurly.com – Subscription management platform ideal for SaaS businesses with recurring billing needs.
- PriceIntelligently: https://www.priceintelligently.com – Provides subscription pricing optimization research and strategies for SaaS businesses.
10. New Service Ideas
Idea 1: CareerCompass
Overview
CareerCompass is a comprehensive career planning and development platform that helps professionals chart their career paths and acquire the skills needed to reach their goals. The service analyzes current job market trends, the user’s existing skills and experience, and their career aspirations to create personalized skill development roadmaps. It then recommends specific courses, certifications, projects, and networking opportunities tailored to their career objectives. The platform continuously updates recommendations based on changing market conditions and user progress, effectively serving as a dynamic career GPS.
Who is the target customer?
▶ Early to mid-career professionals looking to advance strategically
▶ Career changers seeking efficient paths into new industries
▶ College students and recent graduates planning their early career moves
▶ Professionals in industries experiencing rapid technological disruption
What is the core value proposition?
Career advancement requires more than just applying to jobs—it demands strategic skill development and careful planning. Many professionals struggle to identify which skills will provide the highest return on investment for their specific career goals, resulting in wasted time and resources on irrelevant training. CareerCompass solves this by analyzing millions of career trajectories and current job market data to identify the precise skills, certifications, and experiences that create the shortest path to specific career objectives. Users receive a personalized roadmap that demystifies career advancement, turning an overwhelming process into a series of actionable steps with clear ROI.
How does the business model work?
• Base Subscription ($15/month): Access to personalized career path planning, skill gap analysis, and basic course recommendations
• Premium Subscription ($30/month): All base features plus priority industry updates, advanced roadmap customization, and quarterly career strategy sessions with AI coaching
• Enterprise Licenses: Custom pricing for companies to offer the platform to employees as part of professional development programs
• Affiliate Revenue: Commission from recommended learning platforms and certification programs when users enroll through CareerCompass
What makes this idea different?
Unlike traditional career counseling that relies on generic advice or outdated knowledge, CareerCompass leverages real-time market data and AI analysis to provide truly personalized guidance. While competitors like LinkedIn Learning recommend courses based primarily on popularity or broad job titles, CareerCompass creates comprehensive development strategies based on specific career outcomes. The platform doesn’t just recommend skills—it creates a holistic strategy incorporating formal education, practical experience, networking opportunities, and strategic job moves. The continuous updates based on both user progress and market changes ensure recommendations remain relevant, creating a dynamic service rather than a static plan.
How can the business be implemented?
- Develop data integration with job platforms to analyze skill demand trends across industries and roles
- Build AI models that can map career progression paths based on anonymized professional profile data
- Create an intuitive assessment system to accurately capture users’ existing skills, experiences, and career aspirations
- Establish partnerships with education providers, certification bodies, and online learning platforms
- Implement a feedback loop system to track user outcomes and continuously improve recommendation algorithms
What are the potential challenges?
• Data quality and availability for niche industries may limit effectiveness for certain career paths; address by prioritizing data acquisition for high-demand sectors first
• Demonstrating clear ROI may be difficult given the long-term nature of career development; address by implementing milestone tracking and short-term achievement markers
• Maintaining current recommendations in rapidly evolving fields requires significant ongoing data analysis; address by implementing automated trend detection systems and industry specialist review
Idea 2: InterviewMaster
Overview
InterviewMaster is an AI-powered interview preparation platform that creates customized interview simulations based on specific job postings, company research, and user background. The platform analyzes job descriptions to identify likely interview questions, creates company-specific simulations based on known interview patterns, and provides personalized coaching tailored to the user’s experience level and communication style. After each practice session, the system offers detailed feedback on content, delivery, and communication patterns, with specific improvement recommendations. The service bridges the gap between securing an interview and acing it, addressing a critical pain point in the job search process.
Who is the target customer?
▶ Active job seekers with upcoming interviews
▶ Professionals looking to improve interview performance after rejections
▶ Career changers entering unfamiliar interview environments
▶ College students preparing for first professional interviews
What is the core value proposition?
Interview preparation typically relies on generic advice or depends on access to professional networks for insider knowledge. This leaves many candidates—particularly those changing industries or early in their careers—at a significant disadvantage. Poor interview performance leads to rejection despite having the right qualifications, creating frustration and career setbacks. InterviewMaster solves this by creating hyper-specific interview simulations based on the actual job description, company research, and the candidate’s background. The platform provides professional-level interview coaching at scale, giving users the experience and confidence of dozens of practice interviews tailored to their specific opportunities.
How does the business model work?
• Basic Plan ($29.99/month): Access to unlimited interview simulations and basic feedback
• Premium Plan ($49.99/month): Enhanced features including video analysis, industry-specific question banks, and detailed communication coaching
• Single Interview Prep Package ($39.99): One-time purchase for preparation for a specific upcoming interview
• Career Services Partnerships: Licensing to universities and career centers to offer the service to their students/clients
What makes this idea different?
Unlike generic interview question databases, InterviewMaster creates dynamically generated simulations specific to each job opportunity. The platform goes beyond content preparation to address delivery aspects including tone, pacing, and non-verbal communication—elements that generic preparation resources typically ignore. The service integrates research on specific company culture and interview styles, providing insider knowledge typically only available through personal networks. Most significantly, the AI provides personalized, actionable feedback that improves with each practice session, creating a learning curve that generic resources cannot match.
How can the business be implemented?
- Develop an AI engine capable of analyzing job descriptions to identify key skills, requirements, and likely interview focus areas
- Create a comprehensive database of company-specific interview practices through public research and user-contributed data
- Build natural language processing capabilities to evaluate response quality, relevance, and delivery characteristics
- Implement video and audio analysis for non-verbal communication assessment in premium tiers
- Establish feedback mechanisms from users who complete real interviews to continuously improve prediction accuracy
What are the potential challenges?
• Creating truly company-specific simulations requires extensive data that may be unavailable for smaller organizations; address by focusing on industry patterns for less-documented companies
• Video and audio analysis requires substantial computing resources that may impact pricing structure; address by implementing tiered access to these features
• User expectations management is critical as no simulation can perfectly predict actual interview questions; address through transparent communication about prediction methodology
Idea 3: SkillStack
Overview
SkillStack is a portfolio-centric professional network that replaces traditional resumes with verified skill demonstrations through practical projects and challenges. The platform allows professionals to showcase their abilities through completed work samples, verified skill assessments, and peer-reviewed contributions. For employers, SkillStack provides a talent discovery system based on demonstrated capabilities rather than self-reported experience, enabling more accurate matching of candidates to opportunities. The platform ultimately aims to create a more meritocratic hiring ecosystem that values demonstrated ability over credentials or employment history.
Who is the target customer?
▶ Skilled professionals without traditional credentials or career paths
▶ Employers frustrated with inaccurate resumes and poor hiring outcomes
▶ Career changers whose new skills aren’t reflected in their work history
▶ Project-based professionals such as developers, designers, and creative workers
What is the core value proposition?
Traditional resumes and professional profiles suffer from critical limitations: they rely on self-reported information, emphasize credentials over capabilities, and poorly represent practical skills. This creates a fundamental inefficiency in hiring, where candidates struggle to accurately showcase their abilities while employers struggle to identify truly qualified talent. SkillStack solves this by shifting focus from claimed experience to demonstrated abilities. For professionals, this provides a platform to showcase actual skills regardless of how they were acquired. For employers, it reduces hiring risk by providing evidence-based assessment of candidate capabilities, ultimately creating more successful matches between talent and opportunities.
How does the business model work?
• Free Basic Membership: Create a profile, complete public challenges, and maintain a basic portfolio
• Premium Membership ($15/month): Access to advanced skill verification, featured portfolio placement, and direct employer connections
• Employer Subscriptions ($299-$999/month): Talent search access, custom challenge creation, and candidate outreach
• Enterprise Solutions: Custom pricing for large organizations integrating the platform into their broader hiring processes
What makes this idea different?
Unlike LinkedIn and traditional professional networks that prioritize connections and career history, SkillStack focuses exclusively on demonstrated capabilities through real projects and challenges. While portfolio sites like Behance or GitHub serve specific industries, SkillStack creates a cross-disciplinary platform with standardized skill verification applicable to diverse professions. The platform introduces objective credential alternatives through peer review and skill challenges, creating trust mechanisms unavailable in self-reported profiles. Most distinctively, SkillStack inverts the traditional hiring funnel by allowing evidence of capability to precede resume screening, fundamentally changing how talent is discovered.
How can the business be implemented?
- Develop a taxonomy of verifiable skills across various professional domains
- Create a portfolio system that effectively showcases different types of work product and skill demonstrations
- Implement skill verification protocols including peer review, standardized challenges, and evidence validation
- Build employer search tools that match demonstrated skills to job requirements
- Establish partnerships with industry associations and educational institutions for skill standard development
What are the potential challenges?
• Creating equitable verification methods across diverse professional fields requires significant domain expertise; address by starting with technology and creative fields before expanding
• Overcoming ingrained hiring practices and resume dependency requires significant employer education; address through case studies demonstrating improved hiring outcomes
• Preventing gaming of the skill verification system requires robust anti-fraud measures; address through multi-factor verification and statistical anomaly detection
Disclaimer & Notice
- Information Validity: This report is based on publicly available information at the time of analysis. Please note that some information may become outdated or inaccurate over time due to changes in the service, market conditions, or business model.
- Data Sources & Analysis Scope: The content of this report is prepared solely from publicly accessible sources, including official websites, press releases, blogs, user reviews, and industry reports. No confidential or internal data from the company has been used. In some cases, general characteristics of the SaaS industry may have been applied to supplement missing information.
- No Investment or Business Solicitation: This report is not intended to solicit investment, business participation, or any commercial transaction. It is prepared exclusively for informational and educational purposes to help prospective entrepreneurs, early-stage founders, and startup practitioners understand the SaaS industry and business models.
- Accuracy & Completeness: While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information, there is no guarantee that all information is complete, correct, or up to date. The authors disclaim any liability for any direct or indirect loss arising from the use of this report.
- Third-Party Rights: All trademarks, service marks, logos, and brand names mentioned in this report belong to their respective owners. This report is intended solely for informational purposes and does not infringe upon any third-party rights.
- Restrictions on Redistribution: Unauthorized commercial use, reproduction, or redistribution of this report without prior written consent is prohibited. This report is intended for personal reference and educational purposes only.
- Subjectivity of Analysis: The analysis and evaluations presented in this report may include subjective interpretations based on the available information and commonly used SaaS business analysis frameworks. Readers should treat this report as a reference only and conduct their own additional research and professional consultation when making business or investment decisions.

No comment yet, add your voice below!