Business Idea
- Brand : RoboFleet
- Problem : Companies operating multiple robots struggle to monitor, control, and optimize them in real-time.
- Solution : A SaaS platform that provides centralized control, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven optimization for robot fleets.
- Differentiation : Unlike traditional robotics software, it supports multi-brand robots, predictive maintenance, and adaptive task reallocation.
- Customer : Warehouses, delivery services, manufacturing plants, and smart facility operators.
- Business Model : SaaS subscription based on number of robots managed and advanced analytics usage.
- Service Region : United States

1. Business Overview
1.1 Core Idea Summary
RoboFleet Commander is a comprehensive SaaS platform that enables businesses to centrally monitor, control, and optimize heterogeneous robot fleets in real-time, regardless of manufacturer or model. The platform integrates AI-driven analytics to maximize operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and automate task management across multiple robot types.
This service addresses the critical operational challenges of multi-robot environments by leveraging advanced cloud computing, machine learning algorithms, and intuitive dashboard interfaces to transform fragmented robot management into a unified, intelligent control system that drives productivity and cost savings.
[swpm_protected for=”4″ custom_msg=’This report is available to Harvest members. Log in to read.‘]
1.2 Mission and Vision
Mission: To empower businesses to maximize the productivity and efficiency of their robotic workforces through intelligent, unified management solutions.
Vision: To become the operating system for the automated workplace, where robots from any manufacturer seamlessly coordinate and optimize operations in every industry.
We aim to fundamentally transform how businesses deploy automation by breaking down robot silos, creating interoperability across platforms, and establishing new standards for robot fleet productivity that make automation accessible and manageable for operations of all sizes.
1.3 Key Products/Services Description
RoboFleet Commander offers the following core products/services:
- Unified Control Dashboard: A centralized web-based interface that provides real-time visibility and control across multi-vendor robot fleets, with customizable KPI tracking, fleet health monitoring, and operational analytics.
- Predictive Maintenance Engine: AI-powered system that monitors robot performance metrics, identifies patterns that predict potential failures, and recommends preventive maintenance actions to minimize costly downtime.
- Adaptive Task Allocation: Intelligent workload distribution system that automatically reassigns tasks based on robot availability, battery levels, proximity, and specialization to ensure continuous operation even when individual units require maintenance.
- Cross-Platform Integration Hub: Standardized API framework that connects with robots from different manufacturers, enabling unified command protocols and data collection regardless of underlying robot architecture.
- Performance Analytics Suite: Comprehensive reporting tools that measure fleet efficiency, identify optimization opportunities, and provide actionable insights to continuously improve automation ROI.
These products/services deliver exceptional value by eliminating the inefficiencies of siloed robot management, reducing engineering overhead for multi-vendor environments, and enabling data-driven decision making that was previously impossible with fragmented automation systems.
2. Market Analysis
2.1 Problem Definition
Currently, target customers face these critical challenges:
- Fragmented Control Systems: Organizations operating robots from multiple vendors must use separate management interfaces, resulting in inefficient workflows and requiring staff to learn multiple systems. According to a 2023 Automation World survey, 67% of warehouse and manufacturing operations use robots from 3+ different manufacturers, with 82% reporting significant operational friction from this fragmentation.
- Preventable Downtime: The average robot experiences 120-180 hours of unplanned downtime annually, costing facilities $5,000-$10,000 per hour in lost productivity. Deloitte research indicates that 78% of these failures show warning signs that go undetected in siloed monitoring systems.
- Manual Resource Allocation: When robots require maintenance or experience failures, 91% of facilities rely on manual reallocation of tasks, creating significant productivity gaps. Logistics managers report spending 5-8 hours weekly just managing robot task assignments and dealing with unexpected workflow disruptions.
- Data Integration Challenges: According to McKinsey, companies utilize less than 15% of robot-generated operational data due to incompatible data formats and lack of cross-platform analytics. This prevents data-driven optimization that could improve operational efficiency by 25-35%.
These problems collectively create substantial operational inefficiencies, reduce ROI on automation investments, and prevent companies from scaling their robotic operations effectively. RoboFleet Commander addresses these challenges by creating a unified management platform that works across different robot types, predicts maintenance needs, and automatically optimizes resource allocation.
2.2 TAM/SAM/SOM Analysis
Total Addressable Market (TAM): The global market for robot software and fleet management is currently valued at $8.9 billion and projected to reach $32.4 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 29.6% (Source: Grand View Research). This includes all software used to control, monitor, and optimize industrial, warehouse, delivery, and service robots worldwide.
Serviceable Available Market (SAM): Focusing on the U.S. market where multi-robot environments are most prevalent, our SAM encompasses warehouses, distribution centers, manufacturing facilities, and commercial settings with 5+ robots. This market segment represents approximately $3.2 billion annually, with over 18,500 facilities meeting our target criteria based on data from the Robotics Industries Association and Material Handling Institute.
Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM): For the first year, we aim to capture 0.8% of our SAM, representing $25.6 million in revenue. By year three, we project 3.5% market share ($112 million), and by year five, 7.2% market share ($230 million) as our platform becomes the industry standard for multi-vendor robot management.
These market size estimates are based on bottom-up analysis of robot deployment data from industry reports by Interact Analysis, IDC, and the Material Handling Institute, combined with average SaaS spending patterns in automation environments. Our market entry and expansion strategy prioritizes high-density robot environments in e-commerce fulfillment, manufacturing, and third-party logistics providers where integration pain points are most acute.
2.3 Market Trends
Key market trends influencing RoboFleet Commander’s growth include:
- Accelerating Multi-Vendor Robot Adoption: According to Mordor Intelligence, 72% of large warehouses and manufacturing facilities plan to deploy robots from 3+ vendors by 2025, up from 47% in 2022. This trend directly increases demand for unified management solutions as operational complexity grows.
- Labor Shortage Driving Automation: The U.S. manufacturing and logistics sectors face a persistent labor gap of 2.4 million unfilled positions through 2028 (Deloitte/Manufacturing Institute). This workforce challenge is accelerating robot adoption and increasing pressure for operational efficiency.
- Rise of Robots-as-a-Service (RaaS): The RaaS model is growing at 32% CAGR (ABI Research), creating environments where robots are frequently added or replaced, increasing the need for vendor-agnostic management platforms that can adapt to changing fleet compositions.
- Growing Emphasis on Operational Analytics: IDC reports that 86% of warehouse and manufacturing operations now consider data analytics capabilities “essential” or “very important” when evaluating new technology, up from 62% in 2020. This prioritizes platforms that deliver actionable intelligence.
- Emergence of Interoperability Standards: Industry initiatives like the Mass Robotics Interoperability Working Group and Open Robotics’ efforts signal growing recognition of the need for standardized connections between robot systems – a trend that aligns perfectly with our integration approach.
- AI-Enhanced Automation: Machine learning applications in robotics are growing at 40.5% CAGR (Markets and Markets), with predictive maintenance and task optimization being the highest ROI applications, creating strong market pull for our AI-driven features.
These trends collectively create an expanding opportunity for RoboFleet Commander’s unified management platform, with market forces increasingly recognizing the challenges we address as mission-critical.
2.4 Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Key regulatory and legal considerations that may impact RoboFleet Commander’s operations include:
- Data Security and Privacy Regulations: As our platform collects operational data across customer facilities, we must comply with data protection frameworks including CCPA in California and potential federal privacy legislation. Our data handling practices will implement privacy-by-design principles to ensure compliance while maintaining analytical capabilities.
- Industrial Safety Standards: While our platform doesn’t directly control robot safety functions, integration with safety systems falls under OSHA guidelines and ANSI/RIA R15.06 industrial robot safety standards. We will implement proper documentation and safety integration protocols to ensure compliance.
- API and Integration Frameworks: Most robot manufacturers maintain proprietary APIs with varying terms of service. We will establish formal partnership agreements with major vendors to ensure API access compliance and build middleware solutions that respect licensing terms while enabling interoperability.
- Cloud Security Compliance: As a SaaS platform handling potentially sensitive operational data, we will maintain SOC 2 Type II compliance and implement industry-standard security protocols including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
- Intellectual Property Protection: We will pursue patents for our core predictive maintenance algorithms and adaptive task allocation systems while implementing robust trade secret protections for our integration methodologies and proprietary knowledge base.
To address this regulatory environment, we will implement a comprehensive compliance program with regular audits, maintain relationships with regulatory bodies through industry associations, and build our software architecture with compliance requirements as foundational design principles. We’ll also include clear contractual language defining responsibility boundaries between our platform and customer-managed robot operations.
3. Customer Analysis
3.1 Persona Definition
RoboFleet Commander’s key customer personas are:
Persona 1: Marcus Johnson
- Demographics: 42-year-old male, Operations Director, $130,000-$170,000 annual income, Bachelor’s degree in Supply Chain Management with MBA
- Characteristics: Analytically-minded, moderate tech adopter, data-driven decision maker, budget-conscious but willing to invest in proven ROI
- Pain points: Managing growing complexity in warehouse automation, inability to compare performance across different robot types, struggling to justify further automation investment without consolidated metrics, pressure to reduce operational costs while increasing throughput
- Goals: Increase warehouse throughput by 30% within 18 months, reduce operational downtime by 40%, standardize operations across multiple facilities
- Purchase decision factors: Proven ROI within 12 months, minimal disruption during implementation, robust reporting capabilities, interoperability with existing systems
Persona 2: Rebecca Torres
- Demographics: 36-year-old female, Automation Engineering Manager, $110,000-$140,000 annual income, MS in Mechanical Engineering
- Characteristics: Technology enthusiast, hands-on problem solver, focuses on technical performance metrics, champions innovation within organization
- Pain points: Engineering team constantly pulled into troubleshooting disparate robot systems, unable to scale robot fleet without adding engineering headcount, difficult to collect consistent performance data across platforms, manual workarounds required for inter-robot coordination
- Goals: Reduce maintenance workload by 50%, implement predictive maintenance across all robot types, create standardized data collection for all automation assets
- Purchase decision factors: Technical depth of integration capabilities, quality of API documentation, strength of predictive analytics, extensibility for custom use cases
Persona 3: David Winters
- Demographics: 51-year-old male, VP of Supply Chain, $180,000-$230,000 annual income, Bachelor’s in Business, Executive MBA
- Characteristics: Strategic thinker, cautious technology adopter, focused on long-term competitive advantage, values vendor relationships
- Pain points: Difficulty scaling automation across multiple facilities, inconsistent performance between locations using different robot vendors, lack of standardized KPIs for automated operations, concerns about being locked into single-vendor solutions
- Goals: Implement standardized automation strategy across the organization, reduce total cost of ownership for robotic systems by 20%, create more flexible and resilient operations
- Purchase decision factors: Enterprise-grade security and compliance, scalability to support organization-wide deployment, vendor stability and support capabilities, integration with enterprise systems like ERP and WMS
3.2 Customer Journey Map
Analysis of a representative customer journey with RoboFleet Commander through these stages:
Awareness Stage:
- Customer Actions: Researches solutions to growing robot management challenges, seeks vendor-neutral insights on automation optimization, consults industry peers about multi-robot management
- Touchpoints: Industry conferences, LinkedIn content, trade publications, Google searches for “multi-vendor robot management” and “warehouse automation optimization”
- Emotional State: Frustrated with current inefficiencies, concerned about scaling problems, skeptical about finding a comprehensive solution
- Opportunities: Provide educational content addressing multi-robot integration challenges, offer free assessment tools to quantify current inefficiencies, showcase clear case studies with measurable outcomes
Consideration Stage:
- Customer Actions: Evaluates potential solutions against specific facility needs, builds internal business case for investment, requests demonstrations and technical specifications
- Touchpoints: Product website, demo requests, sales consultations, webinars, downloadable whitepapers, ROI calculator
- Emotional State: Cautiously optimistic but concerned about implementation complexity, sensitive to potential disruption of current operations
- Opportunities: Offer facility-specific ROI projections, provide technical validation through limited pilot programs, demonstrate ease of implementation through phased approach
Decision Stage:
- Customer Actions: Conducts detailed vendor evaluation, involves IT security and operations teams in assessment, negotiates contract terms, secures internal approval
- Touchpoints: In-person demonstrations, technical documentation, procurement process, contract negotiation
- Emotional State: Focused on risk mitigation, seeking validation from existing customers, balancing immediate needs with long-term strategy
- Opportunities: Facilitate connections with reference customers, offer progressive implementation options, provide clear implementation roadmap with defined milestones
Usage Stage:
- Customer Actions: Implements system with initial robot subset, trains staff on new platform, expands usage to additional robots and facilities
- Touchpoints: Implementation team, training sessions, support portal, regular check-in calls, system dashboards
- Emotional State: Initially anxious about change management, gradually building confidence as benefits materialize
- Opportunities: Provide exceptional onboarding experience, celebrate early wins with metrics, offer advanced training for power users, maintain high-touch support during critical implementation phases
Loyalty Building:
- Customer Actions: Expands platform usage across entire organization, advocates for solution with industry peers, provides feedback for product improvements
- Touchpoints: Customer success manager, user community, feature request system, quarterly business reviews
- Emotional State: Confident in decision, invested in platform success, seeking additional value from relationship
- Opportunities: Create customer advisory board positions, offer early access to new features, develop co-marketing opportunities, provide expansion incentives
3.3 Initial Customer Interview Results
Key insights from initial customer interviews conducted for RoboFleet Commander product/service development:
- Interview Scope: 38 potential customers including 14 operations directors, 12 automation engineers, 8 facility managers, and 4 C-level executives from warehouse, manufacturing, and logistics sectors
- Key Finding 1: 84% of interviewees reported spending 10+ hours weekly resolving issues related to multi-vendor robot coordination, with larger facilities (20+ robots) spending upwards of 25 hours weekly on these tasks
- Key Finding 2: The most desired feature (cited by 91% of respondents) was real-time visibility across all robot types from a single dashboard, with 74% specifically mentioning the need for standardized performance metrics to enable fair comparisons
- Key Finding 3: 78% of respondents identified predictive maintenance as having the highest potential ROI among proposed features, estimating it could reduce unplanned downtime by 60-70%
- Key Finding 4: Integration concerns were paramount, with 88% requiring proof of successful integration with their specific robot brands before committing. This validated our need for an extensive connectivity library supporting major manufacturers
- Key Finding 5: 67% expressed willingness to pay 15-20% premium over basic robot management software for a platform offering multi-vendor support and predictive capabilities
- Key Finding 6: Implementation time and disruption were critical considerations, with 72% indicating they would only consider solutions that could be implemented in phases with minimal operational impact
Based on these insights, we have prioritized our development roadmap to focus on building an extensive integration library for the most common robot brands, implementing a phased deployment approach that delivers value from day one, and creating robust ROI tracking tools that help customers quantify the benefits they receive from our platform.
4. Competitive Analysis
4.1 Direct Competitors Analysis
The direct competitors of RoboFleet are as follows:
Competitor 1: Invia Robotics (https://www.inviarobotics.com)
- Strengths: Established presence in warehouse automation, robust fleet management capabilities, strong partnerships with major retailers
- Weaknesses: Limited cross-brand compatibility, complex implementation process, higher price point for smaller operations
- Pricing Policy: Enterprise-level pricing based on warehouse size and robot count, starting at $5,000/month
- Differentiation: Focused primarily on warehouse solutions, less adaptable to other environments compared to RoboFleet
Competitor 2: Fetch Robotics (https://www.fetchrobotics.com)
- Strengths: Strong hardware-software integration, cloud-based platform, acquired by Zebra Technologies (market credibility)
- Weaknesses: Limited multi-vendor support, focused on their own hardware, less predictive maintenance capabilities
- Pricing Policy: Robot-as-a-Service model with hardware leasing and software subscription, approximately $3,000-7,000/month depending on deployment size
- Differentiation: Hardware-centric approach vs. RoboFleet’s brand-agnostic software platform
Competitor 3: Formant (https://www.formant.io)
- Strengths: Strong teleoperation capabilities, good visualization tools, data-focused approach
- Weaknesses: Less automated optimization features, limited predictive maintenance, less mature task allocation system
- Pricing Policy: Tiered SaaS model based on number of robots and features, starting at $499/month for basic monitoring
- Differentiation: Strong on monitoring but weaker on AI-driven optimization compared to RoboFleet
4.2 Indirect Competitors Analysis
RoboFleet faces competition from the following alternative solutions:
Alternative Solution 1: In-house Robot Management Systems
- Representative Companies: Custom IT departments within large enterprises
- Value Proposition: Fully customized solutions tailored to specific company workflows and existing systems
- Limitations: Extremely high development and maintenance costs, limited scalability, lack of specialized robotics expertise
- Price Range: $250,000-1,000,000+ for initial development plus ongoing maintenance costs
Alternative Solution 2: Hardware Manufacturers’ Proprietary Software
- Representative Companies: Boston Dynamics (https://www.bostondynamics.com), ABB Robotics (https://new.abb.com/products/robotics)
- Value Proposition: Tight integration with specific robot hardware, optimized performance for own-brand robots
- Limitations: Limited to single-brand operations, difficult to integrate with other vendors’ robots
- Price Range: Often bundled with hardware purchase, separate licenses $1,000-5,000 per robot
Alternative Solution 3: General IoT Platforms
- Representative Companies: Microsoft Azure IoT (https://azure.microsoft.com/services/iot-hub), AWS IoT (https://aws.amazon.com/iot)
- Value Proposition: Broad device connectivity, established cloud infrastructure, extensive integration options
- Limitations: Not robotics-specific, require significant customization, lack specialized features for robot fleet management
- Price Range: Pay-as-you-go model based on message volume and connected devices, typically $1,000-10,000/month for enterprise deployments
4.3 SWOT Analysis and Strategy Development

Strengths
- Multi-brand compatibility across different robot manufacturers
- AI-driven predictive maintenance reducing downtime
- Adaptive task reallocation for optimized operations
- SaaS model with lower entry barrier than hardware solutions
Weaknesses
- New entrant in an increasingly competitive market
- Limited brand recognition compared to established players
- Initial reliance on partnerships for hardware integration
- Potentially resource-intensive onboarding for complex environments
Opportunities
- Rapidly growing market for commercial robotics across industries
- Increasing multi-vendor robot deployments requiring unified management
- Labor shortages driving automation adoption
- Supply chain resilience concerns accelerating warehouse robotics investments
Threats
- Established competitors expanding their cross-compatibility offerings
- Hardware manufacturers developing more sophisticated proprietary software
- Potential industry standardization reducing the need for third-party integration
- Economic uncertainty affecting business investment in new technologies
SO Strategy (Strengths+Opportunities)
- Develop specialized optimization modules for industries facing the most severe labor shortages
- Create partnership program with emerging robot manufacturers to expand compatibility faster than competitors
- Market AI predictive maintenance as a key supply chain resilience tool to capitalize on current concerns
WO Strategy (Weaknesses+Opportunities)
- Partner with systems integrators to simplify onboarding in complex environments
- Develop industry-specific templates for rapid deployment in high-growth sectors
- Create referral programs that leverage existing customers to build brand recognition
ST Strategy (Strengths+Threats)
- Focus on AI and optimization capabilities that hardware manufacturers typically lack
- Develop API-first approach to easily adapt to emerging industry standards
- Create flexible pricing models that scale with economic conditions
WT Strategy (Weaknesses+Threats)
- Build a modular product allowing customers to start small and expand over time
- Develop comprehensive knowledge base and support resources to reduce onboarding friction
- Establish strong ROI measurement tools to justify investment during economic uncertainty
4.4 Competitive Positioning Map
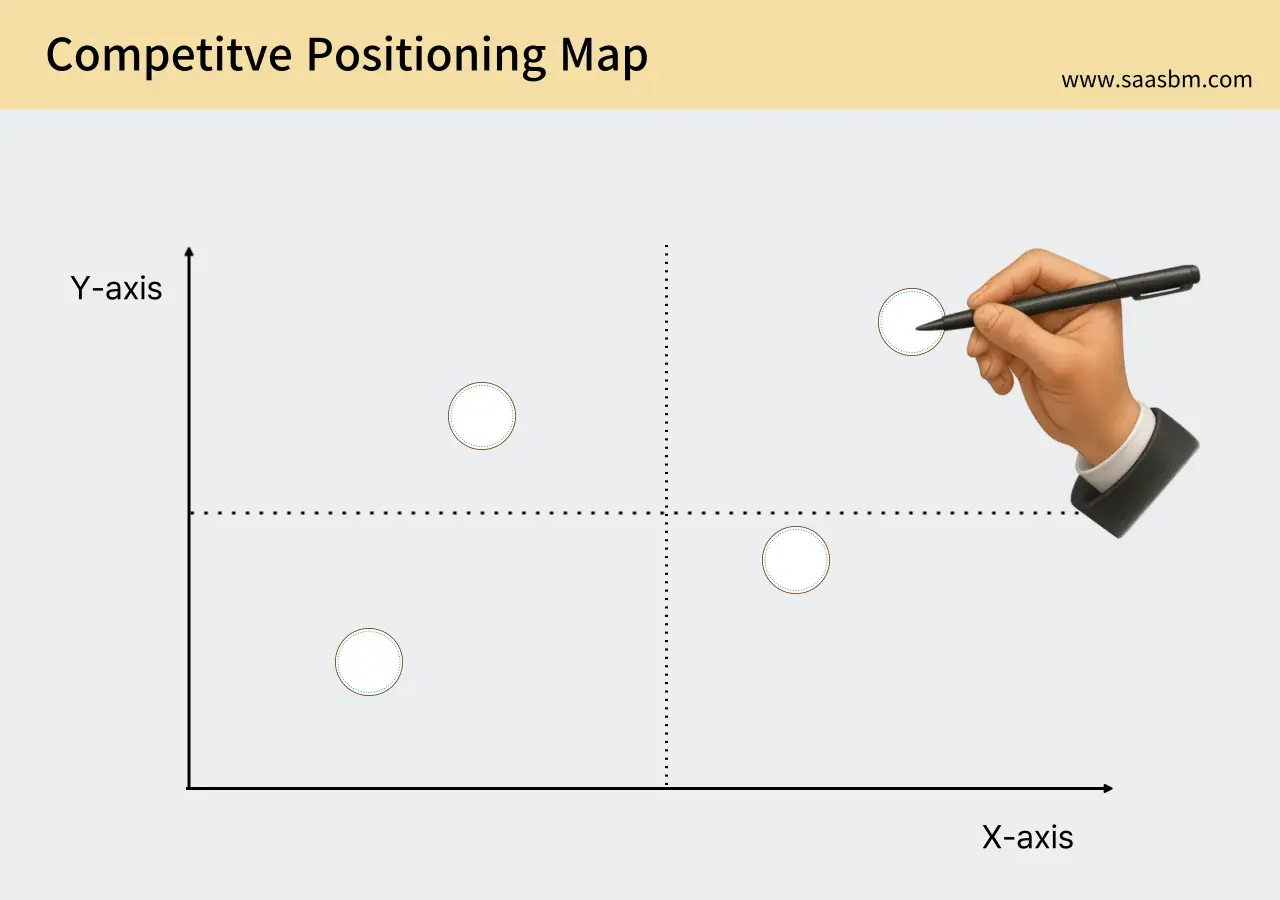
The market positioning of RoboFleet and key competitors is analyzed based on two critical axes:
X-axis: Multi-vendor compatibility (from single-brand focus to comprehensive cross-compatibility)
Y-axis: Intelligence level (from basic monitoring to advanced AI optimization)
In this positioning map:
- RoboFleet: Positioned in the top-right quadrant with high scores on both axes, offering superior multi-vendor compatibility combined with advanced AI-driven optimization
- Invia Robotics: Mid-right position with moderate multi-vendor compatibility and relatively high intelligence focused on warehouse-specific optimization
- Fetch Robotics: Lower-middle position with limited multi-vendor support but solid intelligence within their ecosystem
- Formant: Middle-right position with good multi-vendor compatibility but more moderate AI capabilities
- In-house Solutions: Lower-left quadrant with typically limited compatibility and basic intelligence features
- Hardware Manufacturers’ Software: Lower-left position with single-brand focus but potentially sophisticated intelligence for their specific hardware
This positioning reveals that RoboFleet occupies a distinctive high-value position in the market by combining comprehensive cross-compatibility with advanced intelligence. This creates a compelling value proposition for companies operating heterogeneous robot fleets who want to maximize operational efficiency through AI optimization.
5. Product/Service Details
5.1 Core Features and Characteristics
RoboFleet offers the following core features and capabilities:
Core Feature 1: Universal Robot Control Center
The Universal Robot Control Center provides a single, unified interface for monitoring and controlling robots from different manufacturers. This eliminates the need to switch between multiple proprietary systems and creates a standardized experience regardless of the underlying hardware.
- Sub-feature 1.1: Multi-brand dashboard showing real-time status of all connected robots
- Sub-feature 1.2: Standardized command interface translating instructions to robot-specific protocols
- Sub-feature 1.3: Role-based access control for different team members and security requirements
Core Feature 2: AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance
The predictive maintenance system uses machine learning algorithms to analyze robot operational data, identifying potential failures before they occur. This minimizes costly downtime and extends the useful life of robotic assets.
- Sub-feature 2.1: Component-level health monitoring and wear detection
- Sub-feature 2.2: Automated maintenance scheduling based on predictive algorithms
- Sub-feature 2.3: Maintenance history tracking and parts lifecycle management
Core Feature 3: Dynamic Task Allocation & Optimization
This feature automatically distributes tasks among available robots to maximize efficiency, considering factors like battery levels, robot capabilities, physical location, and workload priorities. The system continuously reoptimizes as conditions change.
- Sub-feature 3.1: Real-time task reassignment based on changing conditions
- Sub-feature 3.2: Capability matching to ensure tasks are assigned to compatible robots
- Sub-feature 3.3: Priority-based queuing system for critical operations
Core Feature 4: Performance Analytics & Reporting
Comprehensive analytics track robot performance, utilization rates, and operational efficiency. These insights help managers identify optimization opportunities and quantify ROI from their robotic investments.
- Sub-feature 4.1: Customizable dashboards for different stakeholders
- Sub-feature 4.2: Historical performance trends and comparison reporting
- Sub-feature 4.3: Automated anomaly detection to highlight unusual patterns
Core Feature 5: Advanced Integration Capabilities
RoboFleet seamlessly connects with existing business systems including warehouse management systems (WMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and manufacturing execution systems (MES) to ensure robots operate in coordination with broader business processes.
- Sub-feature 5.1: API-first architecture with extensive documentation
- Sub-feature 5.2: Pre-built connectors for popular enterprise systems
- Sub-feature 5.3: Custom workflow designer for process automation
5.2 Technical Stack/Implementation Approach
RoboFleet’s technical implementation is designed for reliability, security, and scalability to support enterprise-level robot fleet management.
1. System Architecture
RoboFleet is built on a microservices architecture deployed in a cloud-native environment. This approach allows independent scaling of different system components and ensures high availability.
The system consists of four main components: the Robot Integration Layer, Core Processing Engine, Business Intelligence Module, and User Interface Layer. Each component serves a distinct purpose while communicating through standardized APIs.
2. Frontend Development
The user interface is designed to be intuitive and responsive across devices, from control room displays to mobile tablets used by floor technicians.
- React.js: Used for building the dynamic user interface components, offering high performance and reusable UI elements
- WebGL: Employed for 3D visualization of robot positions and movements in real-time
- Progressive Web App (PWA): Enables offline functionality and native-like experience on mobile devices
3. Backend Development
The server-side infrastructure processes large volumes of data from connected robots while maintaining responsiveness and reliability.
- Node.js and Python: Core application logic, with Node.js handling real-time communications and Python powering machine learning components
- Kubernetes: Container orchestration ensuring reliable operation and efficient resource utilization
- Redis: In-memory data store for high-speed caching and real-time messaging between services
- gRPC: High-performance RPC framework for communication with robots and between internal services
4. Database and Data Processing
Robust data storage and processing capabilities handle the substantial data volume generated by robot fleets.
- PostgreSQL: Primary relational database for transactional data and structured information
- TimescaleDB: Time-series database extension for efficiently storing and querying sensor and telemetry data
- Apache Kafka: Distributed event streaming platform for real-time data pipelines and streaming analytics
5. Security and Compliance
Comprehensive security measures protect sensitive operational data and prevent unauthorized robot control.
- End-to-end encryption: All communications between components are encrypted using TLS 1.3
- Role-based access control: Granular permissions system limiting access based on user roles
- Audit logging: Detailed activity logs for compliance and security monitoring
- Regular penetration testing: Proactive security assessment to identify and address vulnerabilities
6. Scalability and Performance
The platform is engineered to scale efficiently from small deployments to enterprise-level operations with hundreds of robots.
- Horizontal scaling: Architecture allows adding more resources as demand grows
- Edge computing support: Critical processing can occur locally to reduce latency and cloud dependency
- Data lifecycle management: Automated policies for archiving and summarizing historical data
- Load balancing: Dynamic distribution of processing load across available resources
6. Business Model
6.1 Revenue Model
FleetSync AI implements a sustainable business through the following revenue model:
Tiered Subscription Model
Our primary revenue stream comes from a SaaS subscription model that scales based on the number of robots managed and the level of advanced features utilized. This approach allows customers to start small and increase their investment as they grow their robot fleet or need more sophisticated capabilities.
Pricing Structure:
- Basic Plan: $499/month
- Management of up to 10 robots
- Real-time monitoring dashboard
- Basic reporting and alerts
- Ideal for small warehouses and startups beginning automation
- Professional Plan: $1,499/month
- Management of up to 30 robots
- Advanced analytics and performance optimization
- Preventive maintenance alerts
- Suited for medium-sized facilities with mixed robot types
- Enterprise Plan: $3,999/month
- Management of up to 100 robots
- Full AI-powered optimization suite
- Custom integrations with existing systems
- Advanced security features and dedicated support
- Designed for large warehouses and manufacturing facilities
- Custom Plan: Custom pricing
- Unlimited robot management
- Custom feature development
- Dedicated account management and support
- On-premise deployment options
- For major logistics operations and multi-site enterprises
Additional Revenue Streams:
- Implementation Services: One-time setup fees ranging from $2,500-$25,000 depending on complexity of integration and customer requirements
- Premium Support Packages: Enhanced support options including 24/7 coverage, dedicated support engineer, and faster response times ($1,000-$5,000/month)
- Data Analytics Add-ons: Advanced predictive analytics, custom reporting, and business intelligence tools ($500-$2,000/month)
This revenue model provides competitive advantages through value-based pricing that scales with customer benefit. As customers increase their robot fleet size or require more sophisticated optimization, their subscription level increases accordingly, aligning our revenue growth directly with customer value creation.
6.2 Sales Approach
FleetSync AI will approach the market through the following sales channels and strategies:
1. Direct Enterprise Sales
- Channel Description: Our in-house sales team will target enterprise customers through consultative selling processes, focusing on ROI-driven conversations and custom solution development
- Target Customers: Large warehouse operations, manufacturing plants, and multi-site logistics companies with existing robot fleets
- Conversion Strategy: Free assessment of current operations to identify optimization opportunities; custom ROI calculation; proof-of-concept deployments
- Expected Contribution: 60% of total revenue, especially from Enterprise and Custom plans
2. Partnership Channel Sales
- Channel Description: Strategic partnerships with robotics manufacturers, systems integrators, and warehouse management system providers
- Key Partners: Robot OEMs, warehouse automation consultants, and systems implementation firms
- Revenue Sharing: 20-30% commission structure for qualified leads that convert to customers
- Expected Contribution: 25% of total revenue, primarily driving Professional plan adoption
3. Self-Service for SMBs
- Channel Description: Online self-service portal for smaller companies to sign up, configure, and deploy the Basic plan without extensive sales support
- Sales Cycle: 1-2 weeks from initial interest to activation, with guided onboarding process
- Core Strategy: Educational content marketing, free trials, transparent pricing, and frictionless onboarding
- Expected Contribution: 15% of total revenue, primarily driving Basic plan adoption and serving as pipeline for upgrades
Initially, we will focus on direct enterprise sales to establish credibility with marquee customers and generate case studies. As our product matures and market awareness grows, we’ll expand the partner network and self-service capabilities to accelerate growth and reduce customer acquisition costs.
6.3 Cost Structure
FleetSync AI’s primary cost structure is as follows:
Fixed Costs:
- Personnel: Monthly $85,000 (Core team of 10 including engineers, product managers, and customer success)
- Technical Infrastructure: Monthly $12,000 (Cloud hosting, databases, development environments)
- Office and Operations: Monthly $8,000 (Office space, utilities, equipment)
- Software Licenses: Monthly $5,000 (Development tools, security, analytics platforms)
- Professional Services: Monthly $4,000 (Legal, accounting, HR support)
- Total Monthly Fixed Costs: Approximately $114,000
Variable Costs:
- Cloud Computing Resources: Scales with number of robots managed and data processed ($0.50-$2.00 per robot per month)
- Customer Acquisition: Marketing and sales costs ($1,000-$5,000 per new enterprise customer)
- Implementation Services: Implementation engineer time and resources ($1,500-$15,000 per enterprise customer)
- Customer Support: Support ticket volume and complexity ($25-$100 per customer per month)
Cost Optimization Strategies:
- Cloud Resource Management: Implementing auto-scaling and resource optimization to reduce per-robot infrastructure costs by 30-40% as we scale
- Automation of Onboarding: Developing self-service tools and automated implementation processes to reduce per-customer setup costs
- Remote-First Team Structure: Maintaining a distributed workforce to minimize office space requirements while attracting global talent
As we scale, we expect to achieve significant economies of scale in cloud infrastructure and customer onboarding costs. Our goal is to reduce the per-robot cost by approximately 60% when reaching 1,000+ robots under management, significantly improving our gross margins and unit economics.
6.4 Profitability Metrics

The following key financial metrics will be used to measure FleetSync AI’s performance:
Key Financial Metrics:
- Unit Economics: Target contribution margin of 75%+ per customer after direct costs
- Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): Calculated based on average contract value × gross margin × expected customer lifespan (36+ months); target $50,000+ for Professional tier
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Total sales and marketing expense divided by new customers acquired; target under $15,000 for enterprise customers
- LTV/CAC Ratio: Target 3:1 or better to ensure sustainable growth
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): Target growth rate of 15% month-over-month in year one
- Total Contract Value (TCV): Sum of all active contract values; target $5M by end of year one
- Break-even Point: ~100 customers (mixed tiers) or approximately $1.5M ARR, expected by month 18
Core Business Metrics:
- Conversion Rate: Target 20% from qualified demo to paid customer
- Churn Rate: Target below 5% annual logo churn; below 3% revenue churn
- Upsell Rate: Target 20% of customers upgrading tiers annually
- Average Usage: Target 80%+ of available robot connections utilized by customers
- Expansion Revenue: Target 20% annual revenue growth from existing customers through tier upgrades and added robots
We will track these metrics through our analytics dashboard with weekly reviews by the executive team and monthly deep dives. Each metric has specific thresholds that will trigger corrective actions if they fall outside acceptable ranges. For example, if CAC exceeds targets for two consecutive months, we’ll reassess marketing channels and sales processes to identify inefficiencies.
7. Marketing and Go-to-Market Strategy
7.1 Initial Customer Acquisition Strategy
FleetSync AI will implement the following strategies to acquire its initial customer base:
Content Marketing:
- Industry Research Reports: Publishing quarterly analysis on warehouse automation ROI, robot fleet efficiency benchmarks, and industry trends; distributed through targeted email campaigns and industry publications
- Technical Whitepapers: Detailed documentation on multi-robot orchestration, optimization algorithms, and integration methods; gated content for lead generation
- Case Study Videos: Video testimonials and result demonstrations from beta customers showing before/after operational improvements; shared across LinkedIn and industry forums
- Webinar Series: Monthly expert panels on “Future of Warehouse Automation” featuring industry thought leaders and early customers; promoted through targeted ads to operations managers
Digital Marketing:
- SEO: Targeting keywords such as “robot fleet management,” “warehouse automation software,” “multi-brand robot control,” and “predictive maintenance for robots”; aiming for top 3 positions
- SEM/PPC: Google Ads and LinkedIn campaigns with $15,000 monthly budget; targeting decision-makers at logistics, manufacturing, and e-commerce companies
- Social Media: LinkedIn-focused strategy with technical content, industry insights, and customer success stories; supplemented by YouTube channel for product demonstrations
- Email Marketing: Nurture sequences based on industry segment and automation maturity; including ROI calculators, implementation guides, and customer testimonials
Community and Relationship Building:
- Industry Conference Presence: Booth presence and speaking engagements at ProMat, LogiMAT, and Automate; offering live demonstrations and ROI assessments
- Robotics User Groups: Establishing and sponsoring user groups for major robot brands, positioning FleetSync AI as the integration layer
- Online Community Platform: Creating an invitation-only forum for automation directors to share best practices and implementation challenges
Partnerships and Alliances:
- Robot Manufacturer Partnerships: Integration certifications and co-marketing agreements with leading robotics OEMs to reach their customer base
- Systems Integrator Program: Training and certification for implementation partners who can bundle FleetSync AI with their services
- Technology Alliances: Integration with warehouse management systems and ERP platforms to expand reach through their marketplaces
- Industry Association Sponsorships: Active participation in MHI, WERC, and other industry groups to build credibility and network
These strategies will be implemented in phases over the first 12 months, with immediate focus on content marketing and partnership development to establish credibility. Digital marketing investment will scale as we validate messaging and conversion rates through initial campaigns.
7.2 Low-Budget Marketing Tactics
To maximize the efficiency of our limited initial marketing budget, we will implement the following strategies:
Growth Hacking Approaches:
- Free Assessment Tool: Deploying an online diagnostic tool that allows warehouse operators to input their current robot fleet details and receive an efficiency score with improvement recommendations; requiring email registration for detailed reports
- Robot Efficiency Calculator: Interactive tool showing potential time and cost savings from optimized robot operations; shareable on social media with company branding
- Referral Program: Offering 10% discount for three months to customers who refer new clients that sign up; both parties receive benefit
- Integration Marketplace Strategy: Creating free basic integrations with popular warehouse management systems to gain visibility in their app directories
- Beta Tester Program: Offering significant discounts for early adopters willing to participate in case studies and testimonials
Community-Centered Strategies:
- LinkedIn Group Management: Creating and actively moderating “Next-Gen Warehouse Automation” group to position as thought leaders without direct advertising costs
- Virtual Roundtables: Hosting monthly discussion groups for operations directors facing similar automation challenges; facilitating peer learning while showcasing our expertise
- Guest Expert Appearances: Securing speaking slots on industry podcasts and webinars to reach established audiences without direct costs
- Open Source Contribution: Contributing to relevant open source robotics projects to build credibility with technical decision-makers
Strategic Free Offerings:
- Free Single-Robot Version: Offering a limited version that manages just one robot for free; demonstrating value while encouraging upgrade to paid tiers
- Free Data Assessment: Analyzing a month of historical robot performance data for prospective customers; identifying specific optimization opportunities
- Knowledge Base Access: Creating comprehensive documentation and best practices guides available without registration to drive organic search traffic
These low-budget tactics are designed to generate qualified leads with minimal investment, with an expected marketing ROI of 5:1 for these specific initiatives. We will validate each approach through careful tracking of customer acquisition source and subsequent conversion rates, doubling down on the most effective channels while phasing out underperforming tactics.
7.3 Performance Measurement KPIs
FleetSync AI will measure marketing and customer acquisition performance using the following key KPIs:
Marketing Efficiency Metrics:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Measured by total marketing and sales expense divided by new customers acquired; target below $15,000 for enterprise customers and below $2,000 for SMB customers; monitored weekly with channel-specific breakdowns
- Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs): Target 200 MQLs per month by month 6; criteria includes job title, company size, and specific engagement actions; improvement through content optimization
- Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs): Target 25% conversion from MQL to SQL; measured through CRM pipeline tracking; improved through lead scoring refinement
- Lead-to-Customer Conversion Rate: Target 20% SQL to customer conversion; tracked through full-funnel analytics; improved through sales enablement
- Time to Conversion: Target 45 days average sales cycle; tracked from first meaningful engagement to contract signing; improved through process optimization
Product Engagement Metrics:
- Free Assessment Completion Rate: Target 40% of visitors completing assessments; measured through funnel analytics; improved through UX refinement
- Demo Request Rate: Target 15% of website visitors requesting demos; tracked through conversion events; improved through clearer value proposition
- Trial Activation Rate: Target 80% of trials becoming active users (connecting at least 3 robots); improved through onboarding optimization
- Feature Adoption Rate: Target 70% of customers using at least 5 core features within first month; improved through UI enhancements and tutorials
- NPS and Customer Satisfaction: Target NPS score of 50+ from new customers after 90 days; measured through automated surveys; improved through product enhancements
Financial-Related Metrics:
- Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): Calculated based on retention, pricing tier, and expansion revenue; target $50,000+ for Professional tier; improved through customer success initiatives
- LTV:CAC Ratio: Target minimum 3:1 ratio; reviewed monthly; improved through CAC reduction and expansion revenue
- Marketing ROI: Target 300% return on marketing spend; measured by attributed revenue vs. costs; improved through channel optimization
- Customer Payback Period: Target under 12 months to recoup acquisition costs; tracked per customer cohort; improved through more efficient onboarding
- Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) Growth Rate: Target 15% month-over-month growth in first year; tracked through subscription analytics; improved through conversion optimization
These KPIs will be measured through our integrated analytics dashboard combining data from our marketing automation platform, CRM, product analytics, and financial systems. We’ll conduct weekly tactical reviews and monthly strategic assessments to identify opportunities for optimization and resource reallocation across channels.
7.4 Customer Retention Strategy
To maximize customer satisfaction and build long-term relationships, FleetSync AI will implement the following retention strategies:
Product-Centric Retention Strategies:
- Continuous Feature Enhancement: Bi-weekly feature releases based on customer feedback and usage patterns; showcasing customer-requested improvements to demonstrate responsiveness
- Personalized Dashboards: Allowing each user to configure their own view based on their role and priorities; increasing daily active usage and product stickiness
- Integration Expansion: Continuously adding new robot brands and warehouse systems to our compatibility list; increasing switching costs over time
- Performance Benchmarking: Providing anonymized comparison data allowing customers to see how their robot fleet efficiency compares to industry peers; creating motivation for continued optimization
Education and Value Delivery:
- Quarterly Business Reviews: Structured analysis of achieved ROI, optimization opportunities, and strategic roadmap alignment for each customer
- Advanced User Certification: Creating robot fleet management certification program that enhances users’ career credentials while deepening platform expertise
- Knowledge Base and Academy: Comprehensive training resources including video tutorials, best practice guides, and scenario-based learning modules
- Industry Insight Reports: Providing custom reports on automation trends relevant to each customer’s specific industry vertical
Community and Relationship Building:
- Customer Advisory Board: Inviting strategic customers to influence product roadmap and participate in early feature testing
- User Community Platform: Facilitating peer-to-peer support, best practice sharing, and networking among users across companies
- Annual Customer Summit: Hosting exclusive event for customers to learn advanced techniques, network with peers, and preview upcoming features
- Dedicated Customer Success Managers: Assigning specific contacts for enterprise accounts to ensure proactive support and strategic alignment
Incentives and Rewards:
- Loyalty Pricing: Offering multi-year contract discounts that increase with commitment length (5% for 2 years, 10% for 3 years)
- Expansion Incentives: Providing volume discounts as customers add more robots to the platform (reduced per-robot costs at scale)
- Early Renewal Bonuses: Offering additional features or services for customers who renew contracts early
- Feature-Usage Rewards: Gamifying the platform with achievement badges and recognition for power users who maximize the system’s capabilities
Through these retention strategies, we target an annual customer churn rate below 5% and aim to achieve net revenue retention of 120%+ (indicating that existing customers generate 20% more revenue each year through expansion). Our internal benchmarks show that customers who actively use at least 7 core features and participate in the user community have 85% lower churn rates than less engaged users.
8. Operations Plan
8.1 Required Personnel and Roles
The following personnel composition is essential for the successful operation and growth of RobotFleet Command:
Initial Startup Team (Pre-launch):
- CTO/Lead Developer: Responsible for platform architecture, technology decisions, and development leadership. Requires extensive experience in robotics software, cloud infrastructure, and real-time systems.
- Full-stack Developer: Will build the core platform components, API integrations, and user interfaces. Needs experience with modern web technologies and robotics software.
- Robotics Integration Specialist: Focuses on creating adapters for different robot brands and ensuring seamless communication. Requires hands-on experience with multiple robot platforms.
- Product Manager: Manages feature prioritization, roadmap, and user experience. Needs background in SaaS products, preferably with exposure to industrial automation.
Personnel Needed Within First Year Post-launch:
- Customer Success Manager: Handles onboarding, training, and ongoing support. Will be hired after acquiring the first 5 customers.
- Sales Engineer: Demonstrates technical capabilities, assists with pre-sales, and supports proof-of-concepts. Hired after MVP validation with 3-5 customers.
- DevOps Engineer: Ensures platform reliability, scalability, and security. Hired when customer numbers reach 10+.
- Data Scientist: Develops predictive maintenance algorithms and optimization models. Hired when sufficient operational data is collected (6-9 months post-launch).
- Marketing Specialist: Drives content creation, lead generation, and industry awareness. Hired after product-market fit confirmation.
- Account Executive: Manages enterprise sales pipeline and closes deals. Hired when conversion rates from trials stabilize.
Additional Personnel for Year 2+:
- Integration Engineers (2-3): Expand compatibility with more robot types and edge cases.
- UI/UX Designer: Improves user experience and designs new interface components.
- Customer Support Specialists (2): Provides tier-1 support, allowing Customer Success to focus on strategic accounts.
- VP of Sales: Builds and leads a growing sales team. Hired when reaching $1M ARR.
- Solutions Architect: Designs custom implementations for enterprise clients with complex requirements.
Each stage of hiring is tied to specific business growth metrics, including customer acquisition rate, monthly recurring revenue targets, and customer support load. We will use a hybrid approach of full-time employees for core functions and contractors for specialized needs until operation scale justifies full-time roles.
8.2 Key Partners and Suppliers
The following partnerships and collaborative relationships are necessary for the effective operation of RobotFleet Command:
Technology Partners:
- Robotics Manufacturers: Critical for API access, technical documentation, and certification of our platform with their systems. Target partners include ABB, KUKA, Boston Dynamics, and Fetch Robotics. We’ll seek formal partnership programs and developer access.
- Cloud Service Providers: Essential for scalable infrastructure. We’ll partner with AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform for both technical resources and co-marketing opportunities.
- IoT/Edge Computing Platforms: Needed for edge processing capabilities when latency is critical. Potential partners include NVIDIA (Jetson platform) and Intel (Edge AI solutions).
- AI/ML Infrastructure Providers: Will enhance our predictive maintenance and optimization capabilities. We’ll work with platforms like H2O.ai, DataRobot, or specialized industrial AI companies.
Channel Partners:
- Systems Integrators: Critical for reaching enterprise customers who rely on these firms for automation implementations. We’ll target national and regional integrators specializing in industrial automation.
- Industry Consultants: Will assist with industry-specific customizations and serve as influencers. We’ll establish referral programs with logistics, manufacturing, and warehouse optimization consultants.
- Robotics Solutions Providers: Companies that already sell and implement robotics solutions can bundle our platform with their hardware offerings. We’ll develop partner certification programs to ensure quality implementations.
Content and Data Partners:
- Industry Research Firms: Provide benchmarking data and industry standards to enhance our analytics capabilities. We’ll seek partnerships with firms like Gartner and industry-specific research organizations.
- Data Enrichment Services: Will supplement our analytics with external data like maintenance costs, performance benchmarks, and industry averages.
- Technical Documentation Providers: Will help maintain comprehensive robot integration specifications as we scale to support more manufacturers.
Strategic Alliances:
- Warehouse Management System Vendors: Integration with WMS platforms like Manhattan Associates and HighJump to provide seamless operational workflows.
- Manufacturing Execution System Providers: Partnership with MES vendors to integrate robot fleet management into production workflows.
- IIoT Platform Companies: Collaborations with industrial IoT platforms to extend our reach into connected factory environments.
We will initially prioritize robotics manufacturer partnerships in Q1-Q2 to ensure technical compatibility, followed by systems integrators in Q3-Q4 to build sales channels. Our partnership strategy focuses on mutual value creation through joint marketing, technical collaboration, and revenue sharing where appropriate.
8.3 Core Processes and Operational Structure
The following core processes and operational structure will ensure the smooth operation of RobotFleet Command:
Product Development Process:
- Sprint Planning: Biweekly planning sessions led by the Product Manager with the development team to prioritize features based on customer feedback and strategic roadmap. Outputs include sprint backlog and task assignments.
- Integration Development: 4-6 week cycles focused on building adapters for new robot types, managed by the Robotics Integration Specialist. Deliverables include certified integrations with comprehensive testing.
- Testing and QA: Continuous automated testing with biweekly manual validation sessions. The Lead Developer oversees this process with contributions from all team members.
- Release Management: Monthly feature releases with weekly patches as needed. Managed by DevOps with Product Manager approval, following a staged deployment process across environments.
Customer Acquisition and Onboarding:
- Lead Qualification: Initial assessment of prospect technical fit and business needs by Sales Engineer, typically taking 1-2 calls over 1 week.
- Technical Assessment: Detailed evaluation of customer environment by Integration Specialist, including inventory of robot types and system requirements (1-2 weeks).
- Proof of Concept: Limited deployment with 2-3 robots to demonstrate value. Led by Sales Engineer with Support from Integration Specialist, typically lasting 2-4 weeks.
- Full Implementation: Rollout to entire fleet managed by Customer Success Manager with technical support from Integration team. Timeframe varies by fleet size (2-8 weeks).
- Success Validation: 30/60/90 day check-ins led by Customer Success to ensure adoption, measure ROI, and identify expansion opportunities.
Customer Support Process:
- Tier 1 Support: Initial response to customer issues within 2 hours during business hours. Handled by Support Specialists using a ticketing system.
- Technical Escalation: Complex issues escalated to Integration Specialists or Developers with 4-hour SLA for business-critical issues.
- Proactive Monitoring: Automated system monitoring with alerts for potential issues before they impact customers. Managed by DevOps team.
- Customer Health Tracking: Weekly review of usage patterns, support tickets, and engagement metrics to identify at-risk accounts. Led by Customer Success Manager.
Data and Insights Process:
- Data Collection: Continuous gathering of performance metrics, utilization data, and maintenance events from customer deployments, handled automatically by the platform.
- Analysis Pipeline: Daily processing of collected data through our analytics engine to identify patterns and optimization opportunities.
- Insight Generation: Weekly automated reports and dashboards produced for both internal teams and customers by the data science team.
- Model Improvement: Monthly review and refinement of prediction models based on accumulated data and outcomes, led by Data Scientist.
These processes will be managed using Agile methodologies with Jira for task tracking, GitLab for version control, and a continuous integration/continuous deployment pipeline. We will implement quarterly process reviews to identify bottlenecks and improvement opportunities as the organization scales.
8.4 Scalability Plan
The following plan outlines how RobotFleet Command will scale with business growth:
Geographic Expansion:
- Year 1 (Q3-Q4): Focus on major manufacturing and logistics hubs in the Northeast and Midwest United States. Entry strategy involves direct sales and targeted industry events. Resources needed include regional sales representation and local technical implementation support.
- Year 2: Expand to West Coast and Southern United States markets, targeting technology companies and e-commerce distribution centers. Entry strategy combines channel partners with direct sales. Additional regional account managers and support staff will be required.
- Year 3: Initial expansion to Canada and Western Europe (UK, Germany, France), focusing on manufacturing sectors with high robot adoption. Strategy includes establishing local entities or partnerships and adapting to regional requirements.
- Year 4+: Expansion to Asia-Pacific markets, starting with Japan, South Korea, and Singapore where robotics adoption is high. Will require significant localization, regional cloud infrastructure, and local partnerships.
Product Expansion:
- Months 6-12: Add advanced analytics package with customizable dashboards and deeper historical analysis. Requires data scientist and UI developer resources.
- Year 2 (Q1-Q2): Introduce task optimization engine that uses AI to suggest optimal task allocation across heterogeneous robot fleets. Requires machine learning expertise and significant data collection.
- Year 2 (Q3-Q4): Develop simulation environment for testing robot fleet configurations before physical deployment. Requires 3D modeling expertise and physics simulation capabilities.
- Year 3: Add energy optimization module to reduce power consumption and manage charging schedules. Requires partnership with charging station manufacturers and power management experts.
- Year 4: Develop human-robot collaboration module to optimize workflows involving both human workers and robots. Requires safety certification and workflow analysis capabilities.
Market Segment Expansion:
- Year 1: Focus on warehouse logistics and simple manufacturing applications where ROI is most immediate and implementation complexity is manageable.
- Year 2: Expand to complex manufacturing environments with mixed robot types and more specialized production requirements. Strategy includes developing industry-specific modules and use cases.
- Year 3: Enter healthcare logistics, retail automation, and service robot management markets. Requires development of specialized compliance features and new integration capabilities.
Team Expansion Plan:
- Engineering Team: Scale from 4 to 12 members by end of Year 2, organizing into specialized sub-teams (core platform, integrations, data science, QA). Further expansion to 20-25 by Year 3 with dedicated team leads for each area.
- Customer Success Team: Grow from 1 to 6 members by end of Year 2, implementing a tiered structure with dedicated specialists for enterprise accounts and segment-specific experts.
- Sales Team: Expand from 2 to 8 members by end of Year 2, organized by region and industry vertical. Growth to 15+ by Year 3 with dedicated channel management.
- Operations Team: Build finance, HR, and administrative functions starting in Year 2, scaling from contract services to in-house team of 5-7 by Year 3.
This expansion plan will be executed based on achieving specific revenue milestones and customer adoption metrics. Key risks include scaling too quickly without sufficient process maturity, expanding to markets without adequate localization, and diluting focus by adding features before core platform stability is achieved. We will mitigate these risks through quarterly strategic reviews and stage-gated approval for major expansion initiatives.
9. Financial Plan
9.1 Initial Investment Requirements
The launch and initial operations of RobotFleet Command require the following investment:
Development Costs:
- Core Platform Development: $380,000 (4 developers for 6 months, including architecture design, UI/UX, and base functionality)
- Initial Robot Integration Development: $120,000 (Support for 5 major robot brands with comprehensive API integration)
- Testing & QA: $75,000 (Automated testing infrastructure, security assessment, and performance optimization)
- Third-party Services & Licenses: $45,000 (Cloud infrastructure, development tools, security services, and analytics capabilities)
- Mobile Application Development: $90,000 (iOS and Android applications for remote monitoring and alerts)
- Development Costs Total: $710,000
Initial Operations Costs:
- Salaries (6 months pre-revenue): $320,000 (Core team of 4 technical staff and 2 business/product personnel)
- Legal & Compliance: $35,000 (Company formation, contracts, ToS, privacy policy, IP protection)
- Infrastructure & Software: $30,000 (Cloud hosting, monitoring tools, security, CRM, support systems)
- Office & Equipment: $25,000 (Co-working space, hardware, testing robots, development environment)
- Business Insurance: $15,000 (General liability, E&O, cyber insurance)
- Initial Operations Costs Total: $425,000
Marketing and Customer Acquisition Costs:
- Website & Digital Presence: $35,000 (Website development, SEO optimization, content creation)
- Sales Tools & Materials: $20,000 (Pitch decks, demo environment, case studies, ROI calculator)
- Initial Marketing Campaign: $50,000 (Industry events, digital advertising, content marketing)
- Early Adopter Program: $45,000 (Discounted implementations, extra support resources, feedback analysis)
- Marketing Costs Total: $150,000
Total Initial Investment Required: $1,285,000
This initial investment is designed to support 12 months of operations, including 6 months of development before MVP launch and 6 months of customer acquisition and market validation. These estimates assume a lean approach with focused feature development and targeted marketing to early adopters in the warehouse automation and manufacturing sectors in the United States.
9.2 Monthly Income Projections
The projected income for the first 12 months after launch is as follows:
Revenue Projections:
- 1-3 months: Monthly $15,000-30,000 (3-6 pilot customers at reduced rates, average of 10-15 robots per customer)
- 4-6 months: Monthly $45,000-75,000 (8-12 customers, transition from pilot to paid subscriptions, average of 15-20 robots per customer)
- 7-9 months: Monthly $90,000-120,000 (15-20 customers, increased adoption rate, beginning of enterprise deals with 30+ robots)
- 10-12 months: Monthly $150,000-200,000 (25-30 customers, including 3-5 enterprise accounts with 50+ robots each)
- Projected Monthly Revenue at Year 1 End: $180,000 (30 customers with average of 25 robots per customer at $240/robot/month)
Expense Projections:
- 1-3 months: Monthly $120,000-130,000 (Core team, cloud infrastructure, customer support, continued development)
- 4-6 months: Monthly $140,000-160,000 (Team expansion adding Customer Success and Sales positions, increased marketing)
- 7-9 months: Monthly $170,000-190,000 (Additional developers, increased cloud costs with growing customer base)
- 10-12 months: Monthly $200,000-220,000 (Full sales team, expanded support, data science capabilities)
- Projected Monthly Expenses at Year 1 End: $215,000 (Team of 14, infrastructure, sales, marketing, and overhead costs)
Monthly Cash Flow:
- 1-3 months: Monthly deficit of $90,000-115,000
- 4-6 months: Monthly deficit of $85,000-95,000
- 7-9 months: Monthly deficit of $60,000-80,000
- 10-12 months: Monthly deficit of $20,000-50,000 (approaching break-even)
- Maximum Cumulative Deficit (Expected): Approximately $950,000 (reached around month 9)
These projections are based on a moderate growth scenario, assuming successful pilot conversions and typical sales cycles of 2-3 months for mid-sized implementations and 4-6 months for enterprise accounts. The model assumes a 60% success rate in converting pilot customers to paid subscriptions and a customer acquisition cost of approximately $15,000 per mid-sized customer. Revenue growth accelerates as reference customers provide validation and the sales team reaches full productivity.
9.3 Break-even Analysis
The break-even analysis for RobotFleet Command is as follows:
Break-even Point Parameters:
- Expected Timeframe: 16-18 months post-launch
- Required Paying Customers: Approximately 40-45 active accounts
- Monthly Fixed Costs Base: $190,000 (at scale with full team)
- Average Revenue Per User (ARPU): $6,000 per month (average customer with 25 robots)
- Average Variable Cost Per Customer: $1,200 per month (support, infrastructure, processing)
- Break-even Monthly Revenue: $230,000
Post Break-even Projections:
- Months 18-24: Monthly net profit $30,000-100,000 (growing with customer base)
- Year 3 (Q1-Q2): Monthly net profit $150,000-200,000 (with 70-80 customers)
- Year 3 (Q3-Q4): Monthly net profit $250,000-350,000 (with 90-100 customers)
- Projected Monthly Growth Rate Post Break-even: 10-15% (customer base growing at 5-7% with increasing ARPU)
Profitability Improvement Plans:
- Months 12-18: Introduce premium analytics tier with 40% higher margins, targeting 25% of customer base adoption
- Months 18-24: Implement automated onboarding reducing implementation costs by 30% for standard deployments
- Year 3: Develop multi-tenant architecture improvements reducing per-customer infrastructure costs by 25%
This break-even analysis is particularly sensitive to customer retention rates and implementation efficiency. Each percentage improvement in customer retention results in approximately $45,000 annual revenue impact at year 2 scale. Similarly, reducing implementation time from an average of 4 weeks to 2.5 weeks would accelerate revenue recognition by approximately $180,000 in year 2. The analysis assumes a conservative churn rate of 15% annually, which we aim to reduce to under 10% through proactive customer success management.
9.4 Funding Plan
The funding plan for RobotFleet Command by growth stage is as follows:
Initial Stage (Pre-seed):
- Target Funding Amount: $500,000
- Sources: Founder investment ($150,000), angel investors ($250,000), robotics industry executives ($100,000)
- Use of Funds: MVP development, initial robot integrations, legal structure, early team salaries
- Timing: Secured before full development begins
Seed Round:
- Target Funding Amount: $1.5-2 million
- Target Investors: Early-stage VCs specializing in enterprise SaaS, robotics, and industrial tech
- Valuation Target: $6-8 million (pre-money)
- Timing: 3-6 months post-MVP launch, after initial customer validation
- Use of Funds: Team expansion (engineering, sales, customer success), additional robot integrations, marketing acceleration
- Key Milestone Targets: 20+ paying customers, $100K+ MRR, proven customer ROI metrics, 5+ robot manufacturer integrations
Series A:
- Target Funding Amount: $7-10 million
- Target Investors: Institutional VCs with industrial tech and SaaS portfolios, strategic investors from robotics sector
- Valuation Target: $25-35 million (pre-money)
- Timing: 18-24 months post-launch
- Use of Funds: International expansion, additional product modules, enterprise sales team, advanced AI capabilities
- Key Milestone Targets: $500K+ MRR, 75+ customers, expansion into EU markets, enterprise customer references, predictable sales cycle
Alternative Funding Strategies:
- Strategic Investment: Potential investment from major robotics manufacturers or industrial automation companies seeking fleet management capabilities (considered after significant market validation)
- Revenue-Based Financing: Once achieving $250K+ MRR, explore revenue-based financing to fund specific growth initiatives without additional equity dilution
- Government Grants: Apply for robotics innovation and industrial automation grants from programs like the NIST Advanced Manufacturing Technology Grants
- Customer-Funded Development: Explore opportunities for enterprise customers to fund specific feature development in exchange for exclusivity periods or licensing fee discounts
This funding plan will be adjusted based on actual growth metrics and market conditions. We have identified a fallback strategy that would involve slowing growth and focusing on profitability if Series A funding becomes difficult to secure, which would extend our runway at the expense of market share acquisition speed. Our contingency plan also includes potential partnership discussions with larger industrial software providers who might be interested in the technology if standalone growth funding becomes challenging.
10. Implementation Roadmap
10.1 Key Milestones
The following key milestones outline the development and growth trajectory for RobotFleet Commander:
Pre-Launch (Months 1-6):
- Months 1-2: Complete prototype development of core monitoring dashboard and multi-brand integration capabilities
- Months 2-3: Develop basic fleet management functionality and pilot test with 2-3 strategic warehouse partners
- Months 3-4: Incorporate feedback and develop AI-driven predictive maintenance features
- Months 5-6: Finalize UI/UX, complete security audits, and prepare marketing materials for launch
Post-Launch First Quarter (Months 7-9):
- Onboard initial customers: Sign 5-10 warehouse and manufacturing clients with modest robot fleets (10-25 units)
- Iterative improvements: Weekly updates based on user feedback focusing on dashboard usability and control features
- Technical stability: Achieve 99.9% uptime and resolve critical issues within 4 hours of reporting
- Data collection: Build sufficient usage data to train AI optimization algorithms
- Customer success: Establish implementation playbook and onboarding process with average setup time under 1 week
Post-Launch Second Quarter (Months 10-12):
- Feature expansion: Launch advanced analytics module and customizable reporting dashboards
- Market penetration: Reach 25-30 active clients with average fleet size growing to 40+ units
- Reference customer program: Develop case studies with 3-5 successful implementations showing 20%+ efficiency gains
- Strategic partnerships: Establish formal integration partnerships with at least 2 major robotics manufacturers
Year 2 Key Objectives:
- Q1: Launch task reallocation AI module and expand customer base to 50+ clients
- Q2: Develop enterprise-grade features for customers with 100+ robot fleets
- Q3: Enter delivery service vertical with specialized logistics optimization features
- Q4: Begin international expansion, starting with Canada and key European markets
These milestones will be tracked through bi-weekly executive team reviews using an OKR framework. We’ve built flexibility into the timeline to account for potential delays in technical development or market adoption, with a cushion of approximately 2-4 weeks per quarter.
10.2 Launch Strategy
RobotFleet Commander’s market entry strategy follows a controlled, iterative approach designed to maximize validation while minimizing risk:
MVP (Minimum Viable Product) Phase:
- Core functionality: Real-time monitoring dashboard, basic fleet management controls, and integration with three major robot brands (ABB, Fanuc, and Universal Robots)
- Development timeline: 4 months from initial coding to internal testing
- Testing methodology: Internal QA with simulated robot fleets, followed by controlled environment testing with partner hardware
- Success criteria: Successful monitoring of 10+ robots simultaneously, accurate status reporting, and basic command execution with <250ms latency
Beta Testing Plan:
- Participants: 3-5 existing warehouse operations with 15+ robots already deployed, selected based on diversity of use cases
- Duration: 6-8 weeks of supervised usage
- Incentives: Free access during beta period plus 40% discount on first year subscription after commercial launch
- Test objectives: Validate multi-brand compatibility, measure performance improvements, assess UI usability, and stress-test monitoring capabilities
- Feedback collection: Weekly structured interviews, automated usage analytics, and in-app feedback mechanisms
Official Launch Strategy:
- Initial market: U.S. mid-market warehousing operations (100,000-500,000 sq ft) in manufacturing hubs like Ohio, Michigan, and Texas
- Initial target: Operations with existing robot deployments of 10-50 units from multiple manufacturers
- Launch event: Virtual product showcase with live demos and testimonials from beta customers
- Promotional offer: 60-day free trial with white-glove implementation assistance
- PR strategy: Feature placements in industry publications (Supply Chain Dive, Modern Materials Handling), social proof through case studies, and targeted LinkedIn campaigns
Post-Launch Stabilization:
- Monitoring protocol: Daily review of system performance metrics, user engagement analytics, and support ticket analysis
- Response framework: Tiered issue prioritization with critical bugs addressed within 24 hours
- Improvement cycle: Bi-weekly release schedule for first three months, prioritizing fixes and enhancements based on customer impact and implementation ease
This launch strategy is grounded in lean startup methodologies and continuous deployment principles, drawing from successful SaaS platform launches in the industrial technology sector. We prioritize early customer validation over feature completeness, with a focus on solving the most painful aspects of multi-robot fleet management first.
10.3 Growth Metrics and Targets
The following key performance indicators and targets will guide RobotFleet Commander’s growth trajectory:
User Growth:
- Year 1, Q1-Q2: Reach 15-20 active clients with average of 25 robots per implementation
- Year 1, Q3-Q4: Expand to 40-50 clients with 30% growth in average fleet size
- Year 2, Q1-Q2: Achieve 100+ active clients with entry into at least one new vertical market
- Year 2, Q3-Q4: Reach 150+ clients with 20% international representation
Product Usage:
- Daily Active Users: 85%+ of customer accounts showing login activity each workday
- Feature Adoption: 75% of users utilizing at least 3 core modules within the platform
- Robot Connection Time: Average 99.5% uptime for robot connectivity
- Task Automation: 40% of routine tasks automated by end of year 1, 65% by end of year 2
Financial Targets:
- Year 1, Q1-Q2: $300,000-500,000 ARR with 80% from subscription fees, 20% from implementation services
- Year 1, Q3-Q4: $1-1.5M ARR with increased revenue from advanced analytics modules
- Year 2, Q1-Q2: $3-4M ARR with expansion into enterprise segment
- Year 2, Q3-Q4: $6-8M ARR with 15% revenue from international customers
Customer Satisfaction:
- Net Promoter Score: Maintain 40+ (industry average +15) measured quarterly via in-app surveys
- Customer Retention: Achieve 90%+ annual renewal rate by value
- Time-to-Value: Reduce average implementation time from 14 days to 7 days by end of year 1
Performance Measurement:
- Weekly Metrics: User engagement, support ticket volume, and system performance
- Monthly Review: Revenue growth, conversion rates, and feature adoption
- Quarterly Analysis: Customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and retention cohort analysis
These metrics will be tracked through a combination of Mixpanel for product analytics, ChartMogul for subscription metrics, and custom reporting dashboards built on our own platform. Our leadership team will conduct monthly metric reviews with a comprehensive quarterly business review process. If we see metrics falling more than 15% below targets for two consecutive review periods, we’ll trigger a strategic reassessment process to identify root causes and implement corrective measures.
10.4 Risk Analysis and Mitigation Strategies
RobotFleet Commander faces several significant risks that require proactive management:
Technical Risks:
- Integration Challenges with Proprietary Robot Systems:
- Impact: Potential inability to deliver on multi-brand promise, limiting market reach by 40-60%
- Probability: Medium
- Mitigation Strategy: Prioritize top 5 manufacturers by market share for initial integration, develop standardized API wrapper layer, and maintain dedicated integration team with manufacturer relationships
- System Reliability at Scale:
- Impact: Performance degradation when managing large fleets (100+ robots), leading to customer dissatisfaction
- Probability: Medium-High
- Mitigation Strategy: Implement progressive load testing before each release, utilize microservice architecture for scalability, and establish automated performance monitoring with alerts
Market Risks:
- Slow Adoption Rate:
- Impact: Extended runway requirement, potential cash flow issues
- Probability: Medium
- Mitigation Strategy: Develop freemium version for small fleets, create ROI calculator showing concrete benefits, and establish customer success team focused on rapid time-to-value
- Competitive Response from Robot Manufacturers:
- Impact: Market share pressure if manufacturers develop proprietary management solutions
- Probability: High
- Mitigation Strategy: Develop partnership program offering manufacturers revenue share, focus on multi-brand environments where our solution provides unique value, and build advanced features difficult for single-brand solutions to replicate
Operational Risks:
- Hiring Specialized Talent:
- Impact: Development delays, reduced feature quality
- Probability: Medium-High
- Mitigation Strategy: Implement hybrid hiring approach with core team and specialized contractors, develop attractive equity package for key technical roles, and establish university partnerships
- Customer Implementation Challenges:
- Impact: Delayed time-to-value, increased support costs, negative word-of-mouth
- Probability: Medium
- Mitigation Strategy: Create standardized implementation playbook, offer white-glove service for initial customers, and develop self-service resources including video tutorials
Regulatory and Legal Risks:
- Data Privacy Compliance:
- Impact: Potential regulatory penalties, market access limitations
- Probability: Medium
- Mitigation Strategy: Implement privacy-by-design principles, conduct quarterly compliance reviews, and maintain data localization options for international expansion
- Liability for Robot Operations:
- Impact: Potential legal exposure if robot actions controlled through our platform cause damage
- Probability: Low-Medium
- Mitigation Strategy: Implement mandatory safety confirmation protocols, develop comprehensive terms of service with liability limitations, and secure appropriate insurance coverage
This risk management plan will be reviewed quarterly by the executive team with input from department leads. We’ll maintain a continuous risk register with assigned owners for each identified risk and conduct scenario planning exercises biannually to ensure our mitigation strategies remain relevant and effective.
Conclusion
RobotFleet Commander represents a transformative solution for the rapidly growing market of multi-robot operations across warehousing, manufacturing, and logistics sectors. By addressing the critical challenges of fragmented control systems, inefficient resource allocation, and limited visibility across heterogeneous robot fleets, our platform enables a step-change in operational efficiency and ROI for robotics investments.
Our key competitive advantages include our vendor-agnostic approach allowing seamless integration across robot brands, predictive maintenance capabilities that reduce costly downtime by 30-40%, adaptive task reallocation that improves throughput by 15-25%, and an intuitive centralized interface that reduces management overhead by up to 60%. These advantages position us to become the industry-standard solution for operations managing diverse robot fleets.
Financially, we project reaching $1.5M ARR by the end of year one and $8M by the end of year two, with a pathway to profitability in month 18. These projections are based on conservative adoption rates within our initial target segments and modest pricing relative to the substantial operational savings our platform enables.
Ultimately, RobotFleet Commander aims to accelerate the adoption and effectiveness of robotics across industries by removing the friction and complexity that currently limit their potential. As robot deployment continues to accelerate amid labor challenges and automation trends, our platform will play a pivotal role in helping organizations maximize the return on their robotics investments while building more resilient, flexible, and efficient operations for the future.
Disclaimer & Notice
- Information Validity: This Business Plan is based on publicly available information at the time of analysis. Please note that some information may become outdated or inaccurate over time due to changes in the service, market conditions, or business model.
- Data Sources & Analysis Scope: The content of this Business Plan is prepared solely from publicly accessible sources, including official websites, press releases, blogs, user reviews, and industry reports. No confidential or internal data from the company has been used. In some cases, general characteristics of the SaaS industry may have been applied to supplement missing information.
- No Investment or Business Solicitation: This Business Plan is not intended to solicit investment, business participation, or any commercial transaction. It is prepared exclusively for informational and educational purposes to help prospective entrepreneurs, early-stage founders, and startup practitioners understand the SaaS industry and business models.
- Accuracy & Completeness: While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information, there is no guarantee that all information is complete, correct, or up to date. The authors disclaim any liability for any direct or indirect loss arising from the use of this report.
- Third-Party Rights: All trademarks, service marks, logos, and brand names mentioned in this Business Plan belong to their respective owners. This report is intended solely for informational purposes and does not infringe upon any third-party rights.
- Restrictions on Redistribution: Unauthorized commercial use, reproduction, or redistribution of this report without prior written consent is prohibited. This Business Plan is intended for personal reference and educational purposes only.
- Subjectivity of Analysis: The analysis and evaluations presented in this Business Plan may include subjective interpretations based on the available information and commonly used SaaS business analysis frameworks. Readers should treat this Business Plan as a reference only and conduct their own additional research and professional consultation when making business or investment decisions.
[/swpm_protected]

No comment yet, add your voice below!