
- Company : Lawrina
- Brand : Lawrina
- Homepage : https://lawrina.org/
1. Service Overview
1.1 Service Definition
Lawrina is a comprehensive online platform that democratizes access to legal resources and tools through a user-friendly interface designed for both legal professionals and individuals seeking legal assistance.
- Service classification: Legal Technology (LegalTech) SaaS Platform
- Core functionality: Provides accessible legal document templates, guides, educational resources, and tools to streamline legal workflows and make legal knowledge more approachable.
- Founding year: Approximately 2018-2019 (based on website domain registration)
- Service description: Lawrina functions as a multi-faceted legal resource platform that bridges the gap between complex legal processes and everyday users. The platform offers a rich library of customizable legal document templates, comprehensive legal guides written in plain language, and educational resources for various jurisdictions. It provides both free and premium content structured in an intuitive interface that guides users through different legal scenarios and requirements. The service aims to make legal knowledge more accessible while saving time and reducing costs associated with traditional legal services.
[swpm_protected for=”4″ custom_msg=’This report is available to Executive members. Log in to read.‘]
1.2 Value Proposition Analysis
Lawrina delivers value by democratizing legal knowledge and tools, making them more accessible and understandable to both legal professionals and individuals dealing with legal matters.
- Core value proposition: Simplifies access to legal knowledge, documents, and resources in a cost-effective and user-friendly manner, reducing the complexity and expense traditionally associated with legal processes.
- Primary target customers: Lawrina serves two distinct customer segments: (1) Legal professionals seeking efficiency tools and templates to streamline their practice, including solo practitioners, small law firms, and in-house counsel; and (2) Individuals and small business owners who need guidance with legal matters but may not have the resources to hire full legal representation.
- Differentiation points: Lawrina differentiates itself through its dual-audience approach, comprehensive resource library that spans multiple legal areas, plain-language explanations of complex legal concepts, and its balance between free educational content and premium document solutions. The platform’s user experience is designed to be approachable for non-lawyers while still being robust enough for legal professionals.
1.3 Value Proposition Canvas Analysis
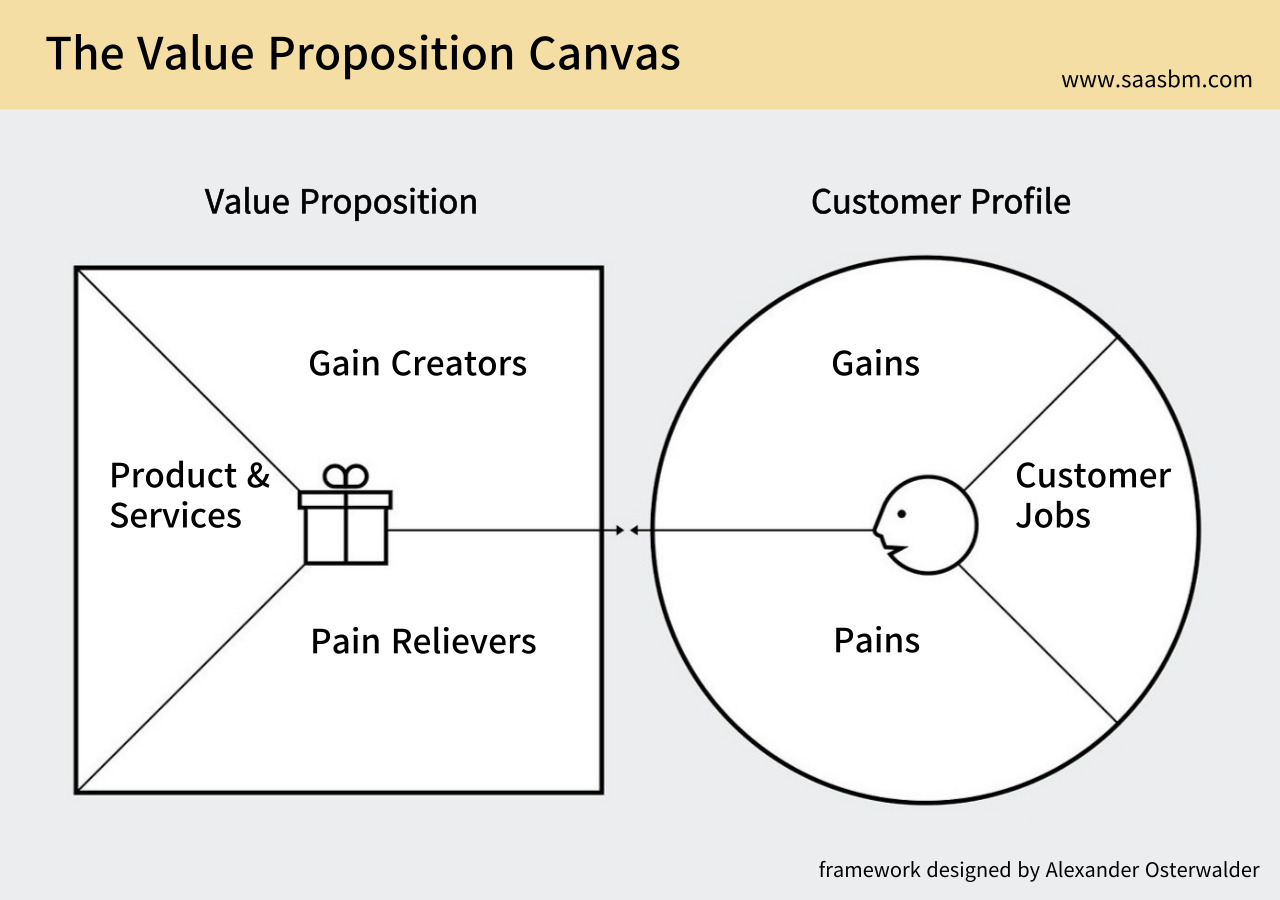
The Value Proposition Canvas systematically analyzes customer needs, difficulties, and expected gains, mapping how Lawrina’s features connect with these elements.
Customer Needs (Jobs)
- Creating legally compliant documents without extensive legal knowledge
- Understanding legal requirements for specific situations or jurisdictions
- Efficiently managing routine legal tasks
- Making informed decisions about when professional legal help is needed
- Staying updated on relevant legal developments and changes
Customer Pain Points (Pains)
- High costs of traditional legal services
- Complex legal jargon and terminology barriers
- Uncertainty about legal requirements and compliance
- Time-consuming nature of legal research and document creation
- Difficulty finding reliable, jurisdiction-specific information
Customer Gains (Gains)
- Cost savings on legal services
- Confidence in legal compliance
- Time efficiency in handling legal matters
- Better understanding of legal processes
- Reduced anxiety when dealing with legal situations
Service Value Mapping
Lawrina effectively addresses customer needs through multiple service components. The document template library directly tackles the pain of high legal costs and time-consuming document creation, while providing the gain of cost savings and efficiency. The educational resources and guides address the pain points of legal complexity and terminology barriers, offering gains in understanding and confidence. The platform’s user-friendly interface and plain-language approach directly combat the pain of legal jargon, providing clarity and reduced anxiety. For legal professionals, Lawrina’s tools streamline routine tasks, addressing efficiency pains while offering time-saving gains. The platform’s comprehensive structure creates a holistic solution where different service elements work together to transform the legal service experience from intimidating and expensive to accessible and manageable.
1.4 Jobs-to-be-Done Analysis
The Jobs-to-be-Done framework examines the fundamental reasons and situations why customers “hire” Lawrina, and their criteria for success.
Core Jobs
Customers “hire” Lawrina primarily to navigate legal matters with greater confidence and reduced cost. Functionally, they need to create legally sound documents, understand legal requirements, and make informed decisions about their legal situations. Emotionally, they seek to reduce anxiety about legal compliance, gain confidence in handling legal matters independently, and feel empowered rather than intimidated by the legal system. Social jobs include appearing competent when dealing with legal matters and avoiding embarrassment from legal missteps.
Job Context
The primary situations driving Lawrina usage include business formation, contract creation, intellectual property protection, and responding to specific legal challenges. For individuals, key contexts include family law matters, real estate transactions, and estate planning. The frequency varies from one-time events (like writing a will) to recurring needs (like drafting regular contracts). The importance is typically high due to the significant consequences of legal errors, creating a scenario where users need reliability but are often price-sensitive. The time pressure can be significant, with many users turning to the platform when facing imminent deadlines or urgent legal needs.
Success Criteria
Users measure success by several key outcomes: documents that are legally valid and accepted by relevant authorities; clear understanding of their legal rights and obligations; confidence in their legal decisions; significant time and cost savings compared to traditional legal services; and smooth legal processes with minimal complications. For business users, success also includes efficient scaling of legal operations, while individual users prioritize peace of mind and accessibility. Both user groups value the ability to complete legal tasks independently while having clear indicators of when professional legal counsel becomes necessary.
2. Market Analysis
2.1 Market Positioning
Lawrina operates in the rapidly evolving legal technology market, positioning itself at the intersection of professional legal tools and consumer-oriented legal resources.
- Service category: Legal Technology (LegalTech) with focus on document automation, legal education, and self-service legal resources
- Market maturity: Growth stage – The legal technology market has moved beyond its initial emergence but hasn’t yet reached full maturity. Traditional legal services are increasingly being disrupted by technology solutions, with adoption accelerating among both legal professionals and consumers. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated digital transformation in legal services, creating expanded opportunities for platforms like Lawrina that bridge physical access gaps.
- Market trend relevance: Lawrina aligns perfectly with several dominant industry trends, including: (1) Democratization of legal information and services; (2) Increasing client demand for fixed fees and transparent pricing; (3) Growing acceptance of DIY and limited-scope legal services; (4) Rising adoption of cloud-based legal solutions; (5) Shift toward plain-language legal communication; and (6) Increasing integration of legal services into broader business workflows.
2.2 Competitive Environment
The legal technology market features various competitors addressing different segments of legal service needs, with Lawrina operating across several competitive zones.
- Major competitors: LegalZoom (comprehensive legal document services with attorney connections), Rocket Lawyer (subscription-based legal services and document creation), Nolo (legal information and DIY solutions), UpCounsel (lawyer marketplace with document capabilities), and Law Insider (contract database and tools for legal professionals)
- Competitive landscape: The LegalTech market is fragmented with different players specializing in specific niches. Large established players like LegalZoom and Rocket Lawyer dominate in consumer awareness but focus heavily on document generation with attorney upsell opportunities. Educational resources are often provided by specialized legal publishers or free resources like FindLaw. The market is experiencing significant investment and innovation, with new entrants focusing on specific verticals (e.g., immigration, intellectual property) or deployment of advanced technologies (AI document review, blockchain for contracts). Pricing models vary widely from freemium to subscription to transaction-based approaches.
- Substitutes: Traditional law firms remain the primary substitute, offering personalized service at premium prices. Other substitutes include: free legal aid organizations; government websites providing basic legal information; general content platforms offering legal articles (but without tools); professional associations providing member-only resources; and DIY methods using generic templates from non-specialized sources.
2.3 Competitive Positioning Analysis
Analyzing the relative positions of Lawrina and its competitors based on key differentiating factors reveals important strategic insights about the platform’s unique market position.
Competitive Positioning Map
The competitive positioning map for the LegalTech space reveals meaningful distinctions between key players based on their service approaches and target audiences.
- X-axis: Scope of legal solutions (Narrow/Specialized to Broad/Comprehensive)
- Y-axis: Primary target audience (Consumer-focused to Professional-focused)
Positioning Analysis
The positioning map reveals distinct strategic approaches among competitors in the LegalTech space:
- LegalZoom: Positioned in the upper-right quadrant with broad service offerings but leaning more consumer-focused. Offers comprehensive document creation with attorney consultation options, but primarily targets individuals and small businesses rather than legal professionals.
- Law Insider: Positioned in the upper-left quadrant with specialized offerings highly focused on legal professionals. Concentrates specifically on contract analysis and language with deep resources for practicing attorneys but limited utility for general consumers.
- Rocket Lawyer: Positioned similarly to LegalZoom in the consumer-focused and broad-service area but with a stronger emphasis on subscription models and slightly more features for small legal practitioners.
- Nolo: Positioned in the lower-right quadrant with consumer focus and relatively broad coverage of legal topics, but with greater emphasis on educational content than practical tools.
- Lawrina: Occupies a distinctive middle-ground position, offering both professional tools and consumer resources across a reasonably broad spectrum of legal areas. This balanced position differentiates Lawrina by serving both audience segments with tailored approaches while maintaining breadth across multiple legal domains.
3. Business Model Analysis
3.1 Revenue Model
Lawrina employs a multi-faceted revenue model that balances free educational content with premium document and tool offerings.
- Revenue structure: Freemium model with transaction-based premium features – Lawrina combines freely available educational content and basic resources with premium paid documents and tools available for individual purchase.
- Pricing strategy: Lawrina uses a tiered document-based pricing approach where users pay for specific templates or resources rather than a full subscription. Prices vary based on document complexity and value, with most document templates ranging from $15-60. Some documents are bundled as packages for related legal needs. The platform occasionally offers promotional discounts to encourage conversion from free content to paid resources.
- Free offering scope: Lawrina provides extensive free content, including educational articles, legal guides, basic legal information, glossaries of legal terms, and simplified explanations of legal processes. Users can browse the document catalog and preview templates before purchasing. The platform also offers some basic calculators and tools without charge. This free content serves as both a customer acquisition channel and establishes the platform’s authority and trustworthiness.
3.2 Customer Acquisition Strategy
Lawrina employs a strategic mix of content marketing, SEO, and educational resources to attract and onboard users efficiently.
- Core acquisition channels: Lawrina’s primary acquisition channels include: (1) Search engine optimization and organic traffic driven by extensive educational content; (2) Content marketing through blogs, guides, and legal resources that address common legal questions; (3) Social media presence highlighting legal tips and resource availability; (4) Strategic partnerships with legal associations, small business organizations, and educational institutions; and (5) Limited paid advertising focusing on specific legal document needs.
- Sales model: Primarily self-service with guided elements – Lawrina employs a product-led growth approach where users can self-navigate the platform and purchase resources without direct sales intervention. The platform guides users through problem identification to appropriate solutions through intuitive navigation and scenario-based organization of resources. For enterprise or organizational clients, the model may include limited inside sales contact for bulk document purchases or custom arrangements.
- User onboarding: Lawrina’s onboarding centers on use-case identification and educational scaffolding. New users are guided to identify their specific legal needs through topic categorization and scenario-based navigation. Free educational content introduces concepts before pushing document purchases, building trust and establishing value. Interactive elements help users determine which specific documents or resources best fit their situation, while tooltips and explanations make legal concepts accessible to non-professionals. The platform employs progressive disclosure to prevent overwhelming new users while still making advanced features discoverable.
3.3 SaaS Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas framework systematically analyzes Lawrina’s overall business structure, illuminating how different elements work together to create and deliver value.
Value Proposition
Simplified access to legal knowledge and documents; cost-effective alternatives to traditional legal services; confidence in legal compliance through user-friendly tools and resources.
Customer Segments
Legal professionals (solo practitioners, small firms, in-house counsel); Individuals with specific legal needs; Small business owners and entrepreneurs; Students and educators in legal fields.
Channels
Web platform; SEO and content marketing; Social media; Email communications; Educational partnerships; Limited paid advertising.
Customer Relationships
Self-service with guided navigation; Educational content building trust; Email follow-ups for document updates; Limited customer support for technical issues.
Revenue Streams
Individual document and template sales; Document package/bundle purchases; Potential enterprise arrangements for organizations; Possible affiliate relationships with legal service providers.
Key Resources
Legal document database and templates; Content creation team with legal expertise; Technology platform and infrastructure; Legal research capabilities; Brand reputation and trustworthiness.
Key Activities
Legal content creation and maintenance; Template development and updating; Platform development and optimization; SEO and content marketing; Legal research and monitoring of legal changes.
Key Partnerships
Legal professionals for content verification; Legal associations and bar organizations; Small business support organizations; Legal technology providers; Educational institutions with legal programs.
Cost Structure
Content creation and legal expertise; Technology development and maintenance; Marketing and customer acquisition; Legal research and template updating; Platform hosting and operations.
Business Model Analysis
Lawrina’s business model demonstrates several significant strengths. The freemium approach with transaction-based premium features allows for low-friction customer acquisition while maintaining clear monetization paths. The model efficiently leverages content marketing and SEO as primary acquisition channels, reducing CAC compared to paid-dominant acquisition strategies. The self-service approach enables scaling without proportional customer support costs. However, the model faces challenges including potential commoditization of legal templates, cyclical or one-time purchase patterns that may limit recurring revenue, and dependency on maintaining fresh, legally accurate content across multiple jurisdictions. The sustainability of the model relies on efficient customer acquisition through content marketing, strategic expansion of document offerings to encourage repeat purchases, and potentially developing more subscription-based elements to increase predictable revenue. Lawrina’s dual focus on both consumers and professionals creates cross-segment opportunities but requires careful balancing of resources and positioning.
4. Product Analysis
4.1 Core Feature Analysis
Lawrina’s platform integrates several distinct feature categories that together create a comprehensive legal resource ecosystem for its users.
- Major feature categories: (1) Legal Document Templates and Forms; (2) Educational Content and Legal Guides; (3) Legal Process Explainers; (4) Jurisdictional Information Resources; (5) Legal Glossary and Terminology Tools; (6) Interactive Legal Tools and Calculators
- Core differentiating features: Lawrina distinguishes itself through its dual-audience approach that offers appropriate resources for both legal professionals and laypeople. The platform’s plain-language explanations that accompany complex legal documents help non-lawyers understand what they’re using. Its comprehensive legal guides go beyond simple templates to provide contextual understanding. The platform employs an intuitive categorization system that organizes resources by life/business events rather than just legal categories, making it easier for non-lawyers to find relevant information.
- Functional completeness: Compared to competitors, Lawrina offers strong breadth across multiple legal domains but with varying depth. Its document template library is substantial but not as extensive as specialized providers like LegalZoom. Its educational content is more comprehensive than most document-focused competitors. The platform provides good coverage of common legal scenarios but may lack depth in highly specialized areas. The absence of direct attorney consultation services (unlike some competitors) is balanced by more extensive self-help resources. Overall, Lawrina achieves a strong balance of breadth and accessibility, though with some depth trade-offs in specialized niches.
Lawrina’s product approach emphasizes making legal resources approachable through contextual explanation and intuitive organization. For example, instead of simply providing a “Power of Attorney” template, the platform explains different types, when each is appropriate, state-specific requirements, and step-by-step completion guidance. This educational scaffolding helps users make appropriate choices rather than just providing raw documents. Similarly, business formation resources include not just incorporation documents but also explanations of entity types, tax implications, and ongoing compliance requirements, creating a more complete solution than mere templates.
4.2 User Experience
Lawrina’s user experience is designed to make legal resources approachable and navigable for users with varying levels of legal knowledge.
- UI/UX characteristics: Lawrina employs a clean, modern interface with clear visual hierarchy and intuitive navigation. The design deliberately avoids the intimidating, text-heavy approach common to legal resources in favor of accessible card-based layouts with ample white space. Color-coding helps users distinguish between different types of resources (educational vs. document templates). The platform uses progressive disclosure to present complex information in digestible chunks, revealing details as users express interest in specific topics. Iconography and visual elements help break up text and guide users through processes.
- User journey: The typical user journey begins with problem identification through either direct search or navigation through topic categories. Users exploring a legal topic typically encounter educational content first, building understanding before being presented with relevant document options. For document acquisition, the platform provides preview capabilities, clear pricing, and contextual guidance before purchase. The document completion process includes inline help, tooltips, and validation to ensure accuracy. Post-purchase, users receive completed documents with additional usage guidance and potential follow-up resources.
- Accessibility and ease of use: Lawrina achieves good accessibility through plain-language explanations of legal concepts, responsive design that works across devices, and an information architecture that doesn’t require legal training to navigate. The platform employs scenario-based pathways (“Starting a Business” or “Planning Your Estate”) that align with how non-lawyers conceptualize legal needs rather than traditional legal categories. For professional users, more advanced filtering and direct category access is available. The complexity level is appropriately tiered, with basic information highly accessible and more nuanced content available as users demonstrate interest in specific areas.
A noteworthy aspect of Lawrina’s user experience is its contextual guidance approach. Rather than forcing users to self-identify their exact legal need (which non-lawyers often struggle with), the platform guides users through a series of plain-language questions about their situation to identify appropriate resources. For example, a small business owner concerned about intellectual property protection would be guided through questions about their specific assets (logos, product designs, written content) before being directed to relevant trademark, copyright, or patent resources. This scenario-based navigation significantly reduces the knowledge barrier that typically makes legal resources intimidating.
4.3 Feature-Value Mapping Analysis
This analysis maps how Lawrina’s key features deliver specific customer value and assesses their differentiation level compared to competitors.
| Core Feature | Customer Value | Differentiation Level |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Document Templates | Provides legally sound documents without attorney costs; saves time in document creation; ensures compliance with current legal requirements | Medium |
| Plain-Language Legal Guides | Builds understanding of legal concepts; reduces anxiety about legal processes; empowers informed decision-making | High |
| Scenario-Based Navigation | Simplifies finding relevant resources; reduces required legal knowledge; mirrors how non-lawyers think about legal issues | High |
| State-Specific Legal Information | Ensures compliance with local regulations; provides jurisdiction-relevant guidance; reduces risk of using inappropriate information | Medium |
| Legal Process Explainers | Creates roadmaps for complex legal journeys; sets accurate expectations; identifies potential pitfalls | High |
| Interactive Legal Tools | Simplifies calculations and decision-making; personalizes general principles to specific situations; provides immediate value before purchase | Medium |
| Legal Terminology Glossary | Demystifies legal jargon; increases confidence in understanding documents; bridges knowledge gap between lawyers and laypeople | Low |
Mapping Analysis
The feature-value mapping reveals Lawrina’s strategic emphasis on making legal concepts and processes understandable and navigable, rather than competing solely on document quantity or specialized depth. The platform’s highest differentiation areas – plain-language guides, scenario-based navigation, and process explainers – all center on reducing knowledge barriers and anxiety around legal matters. This aligns well with the identified customer pain points of legal complexity and terminology barriers. While document templates (the core monetization feature) show only medium differentiation, they gain competitive strength through their integration with the highly differentiated educational scaffolding. This creates a coherent ecosystem where free educational content drives traffic and builds trust, while enhancing the value of the paid document templates. The primary improvement opportunity lies in the interactive tools category, which could be expanded to create more personalized experiences and stronger differentiation. The relatively lower differentiation in the state-specific information suggests an opportunity to deepen jurisdictional coverage as a competitive advantage, particularly for legal professionals who require precise local information.
5. Growth Strategy Analysis
5.1 Current Growth Status
Lawrina appears to be in the growth stage of its product lifecycle, with substantial opportunities for expansion across multiple dimensions.
- Growth stage: Growth Phase – Lawrina shows characteristics typical of a SaaS platform in its growth stage rather than early introduction or full maturity. The platform has established its core value proposition and product-market fit with a substantial content library and established user experience. However, it has not yet reached market saturation or the optimization-focused maturity phase. The ongoing expansion of content areas and features indicates continued product evolution rather than mere refinement.
- Expansion directionality: Lawrina demonstrates multiple viable expansion vectors. Product expansion opportunities exist through deeper content in current legal areas, new specialty legal domains, additional interactive tools, and potentially direct service connections. Market expansion possibilities include greater international/jurisdictional coverage, targeted vertical solutions for specific industries, and enhanced offerings for either the professional or consumer segments. The platform’s dual-audience approach provides flexibility to emphasize either professional or consumer directions based on traction and economics.
- Growth drivers: Several factors are likely driving Lawrina’s current growth trajectory: (1) Increasing willingness of both consumers and professionals to adopt digital legal solutions, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic; (2) Rising legal service costs creating demand for alternative solutions; (3) Content marketing creating a virtuous cycle of SEO visibility, traffic, and domain authority; (4) The scalable nature of the core product allowing revenue growth without proportional cost increases; and (5) The platform’s educational approach building trust and facilitating conversion from free to paid resources.
Lawrina’s current growth pattern appears to leverage content marketing and SEO as primary engines, building a foundation of traffic and authority that enables cost-effective customer acquisition. This approach is particularly suitable for the legal domain where trust is crucial and users often begin with research before seeking specific solutions. The platform seems to employ a progressive engagement model where users initially engage with free educational content before developing the confidence and need to purchase specific document templates. This creates a natural nurturing pipeline that likely requires less aggressive sales tactics than more transactional competitors. The dual focus on both professional and consumer markets provides resilience through market fluctuations while creating some challenges in messaging and positioning. The transaction-based revenue model may create some cyclicality in revenue depending on seasonal legal needs (e.g., tax season, business formation cycles), suggesting potential benefits from developing more recurring revenue components.
5.2 Expansion Opportunities
Lawrina has multiple promising avenues for expansion across product capabilities, market reach, and revenue diversification.
- Product expansion opportunities: Lawrina could enhance its product through several strategies: (1) Deeper coverage of specialized legal niches (intellectual property, immigration, employment law); (2) Development of advanced interactive tools like document assembly with conditional logic; (3) Creation of workflow systems that guide users through multi-step legal processes; (4) Integration of AI-powered features for document review or legal research assistance; (5) Addition of community features allowing peer support and experience sharing; and (6) Development of mobile applications for on-the-go legal resource access.
- Market expansion opportunities: Potential market expansion directions include: (1) Deeper international coverage beyond the current US focus; (2) Development of industry-specific legal packages for verticals like healthcare, technology, or real estate; (3) Creation of specialized resources for emerging areas like cryptocurrency, privacy law, or remote work regulations; (4) Partnerships with educational institutions for legal education applications; (5) Development of specific solutions for underserved segments like non-profit organizations; and (6) Creation of enterprise-focused offerings for in-house legal departments.
- Revenue expansion opportunities: Revenue diversification could come through: (1) Introduction of subscription tiers for frequent document users; (2) Development of premium membership with enhanced features and document access; (3) Creation of white-label or API solutions for partners to integrate legal resources; (4) Facilitation of attorney connections with referral fees (while maintaining independence); (5) Licensing content to educational platforms or other legal services; and (6) Offering custom document packages for specific business types or industries.
Each expansion direction presents distinct advantages and challenges. Product expansions into interactive tools and workflows would increase value and potentially support higher price points, but require significant development resources. Market expansions into international jurisdictions would substantially increase the addressable market but demand expertise in diverse legal systems. Vertical specialization could increase relevance and conversion rates but might narrow overall market reach. Revenue diversifications like subscriptions could create more predictable cash flow but might reduce accessibility for occasional users. The optimal strategy likely involves sequencing these opportunities based on resource requirements, expected return timeframes, and synergies between different initiatives. For example, developing industry-specific packages could simultaneously achieve both product and market expansion while supporting premium pricing, creating an efficient growth vector that leverages existing assets with targeted enhancements.
5.3 SaaS Expansion Matrix
The SaaS Expansion Matrix systematically analyzes Lawrina’s growth paths and prioritizes the most promising directions.
Vertical Expansion (Vertical Expansion)
Definition: Providing deeper value to the same customer base
Potential: High
Strategy: Lawrina could deepen its value proposition to current users through several approaches: (1) Creating more comprehensive legal journey maps that guide users through complex multi-step processes; (2) Developing premium document packages with enhanced customization capabilities; (3) Offering document update services that notify users of relevant legal changes affecting their documents; (4) Creating dashboard tools for managing multiple legal documents and deadlines; and (5) Developing more advanced interactive tools that provide personalized guidance based on user-specific factors.
Horizontal Expansion (Horizontal Expansion)
Definition: Expanding to similar customer segments
Potential: Medium
Strategy: Lawrina could expand horizontally by: (1) Developing targeted resources for adjacent professional groups like accountants, financial advisors, or HR professionals who frequently encounter legal issues; (2) Creating specialized packages for different business types (restaurants, e-commerce, consulting services) with relevant legal resources for each; (3) Expanding language offerings to reach non-English speaking segments within current markets; (4) Developing solutions specifically for remote/distributed businesses facing multi-jurisdictional challenges; and (5) Creating educational resources for legal-adjacent academic programs.
New Market Expansion (New Market Expansion)
Definition: Expanding to new customer segments
Potential: Medium
Strategy: New market opportunities for Lawrina include: (1) International expansion with jurisdiction-specific content for Canada, UK, Australia and other common law countries; (2) Development of enterprise solutions for larger organizations with distributed legal needs; (3) Creation of specific offerings for nonprofit and social enterprise sectors; (4) Building solutions for emerging legal needs in cryptocurrency, blockchain, and digital asset management; and (5) Developing platforms for legal educators to use Lawrina content in academic contexts.
Expansion Priorities
Based on resource requirements, market opportunity, and alignment with current strengths, the recommended expansion priorities are:
- Vertical Expansion through enhanced document journeys and interactive tools – This leverages Lawrina’s current user base and educational strengths while creating opportunities for premium pricing. The implementation can be incremental, with each new feature building on existing foundations and creating immediate value.
- Horizontal Expansion into adjacent professional segments – This expands the addressable market while utilizing existing content with targeted modifications. These segments likely have higher lifetime value and more frequent usage patterns than general consumers.
- New Market Expansion into select international jurisdictions – While offering substantial growth, this requires significant investment in jurisdiction-specific legal expertise. A phased approach starting with Canada (most similar to US law) would allow testing international expansion with minimal legal system differences before venturing into more distinct jurisdictions.
6. SaaS Success Factors Analysis
6.1 Product-Market Fit
This analysis examines how well Lawrina aligns with its target market’s needs from multiple perspectives.
- Problem-solution fit: Lawrina addresses high-priority problems in the legal services market with effective solutions. The problem of legal service accessibility is significant and growing as legal costs continue to rise while DIY legal needs increase. The platform’s combination of templates and educational content effectively addresses both the practical need (document creation) and the knowledge gap that typically prevents self-service in legal matters. This dual approach creates stronger problem-solution fit than competitors focusing solely on documents without context or education without practical tools.
- Target market fit: Lawrina’s dual focus on both legal professionals and individuals/small businesses demonstrates good market selection. Both segments face cost and efficiency pressures with legal matters, though their specific needs differ. The professional segment offers higher potential lifetime value and usage frequency, while the consumer segment provides larger volume potential. This balanced approach creates resilience through market cycles and multiple monetization paths. The platform’s particular strength for solo practitioners and small firms addresses an underserved market between consumer-grade solutions and expensive enterprise legal tech.
- Market timing: Lawrina’s timing appears advantageous within the legal services evolution. The market has progressed beyond initial resistance to online legal services, with both consumers and professionals increasingly accepting digital legal solutions. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated digital adoption in legal services, creating a favorable environment for online platforms. The increasing complexity of regulatory compliance across jurisdictions creates growing demand for accessible legal guidance. However, the market is not yet fully mature or consolidated, providing opportunity for platforms to establish strong positioning before commoditization.
Lawrina’s product-market fit demonstrates particular strength in its educational scaffolding approach. While many competitors offer similar document templates, Lawrina’s emphasis on building understanding alongside practical tools addresses the fundamental challenge preventing wider self-service legal solution adoption: the knowledge gap between legal professionals and laypeople. By progressively building user confidence and competence through educational content before monetizing through document sales, Lawrina creates a more sustainable engagement model than transaction-only approaches. The platform’s balanced attention to both professional and consumer segments creates flexibility to emphasize whichever shows stronger unit economics or growth potential. This dual-market approach also creates opportunities for cross-segment insights, where professional-grade content can be adapted for consumer use and consumer usability principles can enhance professional tools. The primary product-market fit challenge appears to be in clearly communicating this balanced value proposition without diluting appeal to either segment.
6.2 SaaS Key Metrics Analysis
This section analyzes the key operational metrics that determine success for Lawrina’s SaaS business model.
- Customer acquisition efficiency: Lawrina’s content marketing and SEO-focused acquisition strategy appears relatively efficient compared to paid-dominated alternatives. The extensive educational content creates organic traffic and gradual authority building in search results for legal topics. This approach, while slower than aggressive paid acquisition, typically yields more sustainable and cost-effective customer acquisition. The freemium model allows users to experience value before purchase, likely enhancing conversion rates compared to pure paywall approaches. The platform’s educational content serves dual purposes of both acquisition and trust-building, creating efficiency through multipurpose assets.
- Customer retention factors: Lawrina’s stickiness factors include several elements that promote retention and repeat usage. The comprehensive resource library covering multiple legal areas increases the likelihood of users returning for different legal needs over time. The platform’s educational approach builds user confidence and trust, creating preference for familiar resources when new legal needs arise. Document updates based on legal changes provide natural re-engagement opportunities. However, the transaction-based model without a strong subscription component may create challenges in maintaining consistent engagement between specific legal needs.
- Revenue expansion potential: Lawrina shows promising opportunities for expanding revenue per customer. Cross-selling across legal categories is a natural path as users who purchase one document are likely to need others throughout their business or personal legal journey. The platform’s educational content creates opportunities to identify additional user needs beyond their initial purchase intent. The current transaction-based model could be supplemented with subscription tiers for frequent users or premium features. For professional users, expanded document customization capabilities could justify higher price points. Bundles targeting specific scenarios (business formation, intellectual property protection) offer natural upsell opportunities with demonstrated value justification.
Analysis of these key metrics reveals Lawrina’s particular strength in top-of-funnel efficiency through content marketing, creating favorable unit economics compared to paid acquisition-dependent competitors. The educational content serves triple duty as acquisition tool, trust builder, and value demonstrator, creating operational efficiency. The current model likely produces good initial conversion rates from free to paid users due to the clear value demonstration through educational content. The primary metric challenge appears to be in maximizing customer lifetime value, as the transaction-based approach may create inconsistent engagement patterns. Introducing elements like document updates, compliance monitoring, or subscription access to premium features could enhance retention metrics. For professional users, workflow tools that integrate with daily operations would create stronger lock-in effects. The diverse legal needs of users create natural expansion opportunities if the platform effectively tracks user journeys and proactively suggests relevant resources at appropriate times. Implementing triggered recommendations based on both prior purchases and browsing behavior could significantly enhance expansion metrics.
6.3 SaaS Metrics Evaluation
This analysis estimates and evaluates key SaaS business metrics to assess Lawrina’s economic health.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Estimate: Medium-Low
Rationale: Lawrina’s content marketing and SEO-focused approach likely produces CAC lower than competitors relying heavily on paid channels. The extensive educational content creates organic traffic and search visibility without proportional cost scaling. However, content creation in the legal domain requires specialized expertise, creating higher production costs than general content. The SEO approach, while cost-effective long-term, requires upfront investment and patience before yielding results. The legal industry’s relatively high search volumes for specific legal terms like “LLC formation” or “will template” create efficient targeting opportunities.
Industry comparison: Likely better than industry average for legal services, which typically have high customer acquisition costs due to the high-consideration nature of legal decisions and expensive keywords in paid channels.
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
Estimate: Medium with segmentation variance
Rationale: Lawrina’s LTV likely varies significantly between user segments. Professional users would have higher frequency of legal document needs and potentially higher-value purchases, creating stronger LTV. Consumer users likely have more sporadic legal needs but represent larger volume potential. The transaction-based model without strong subscription components may limit predictable recurring revenue, though legal needs do naturally recur through business and life cycles. The educational content likely enhances repeat purchase rates by building platform familiarity and trust.
Industry comparison: Comparable to document-focused legal platforms but potentially lower than subscription-based legal services that create more consistent recurring revenue.
Churn Rate
Estimate: Not directly applicable in traditional sense / Medium activity churn
Rationale: As primarily a transaction-based platform rather than subscription service, Lawrina doesn’t experience churn in the traditional SaaS sense. However, user activity churn (failure to return for additional purchases) is a relevant metric. Activity churn is likely moderate due to the episodic nature of legal needs balanced against the platform’s ability to serve multiple legal categories over a user’s lifecycle. Professional users likely show lower activity churn due to regular document needs, while consumer users may have more extended periods between engagements.
Industry comparison: Likely comparable to other legal document platforms, with lower activity churn than single-purpose legal tools but higher than comprehensive legal subscription services.
LTV:CAC Ratio
Estimate: 3:1 to 4:1 (varying by segment)
Economic analysis: The estimated LTV:CAC ratio suggests a fundamentally viable business model with good unit economics, particularly for the professional segment. The content marketing approach creates favorable acquisition economics compared to paid-dominant strategies. The transaction-based model creates some LTV limitations compared to subscription models but offers lower friction for initial conversion. The ratio likely exceeds the typical 3:1 minimum threshold for SaaS sustainability, though it may not reach the 5:1+ ratios seen in highly optimized SaaS businesses.
Improvement opportunities: The LTV:CAC ratio could be enhanced through several strategies: (1) Implementing subscription options for frequent users to increase predictable revenue; (2) Developing more professional-focused tools that justify premium pricing; (3) Creating document update services that generate recurring revenue; (4) Enhancing cross-selling systems to increase purchases per customer; and (5) Refining content strategy to focus on most efficient customer acquisition topics.
7. Risk and Opportunity Analysis
7.1 Key Risks
Lawrina faces several significant risks that could impact its growth trajectory and long-term sustainability in the legal resources marketplace.
- Market Risks: Rapidly changing legal regulations across jurisdictions could quickly outdated content and templates. The legal tech market is becoming increasingly saturated, with traditional legal service providers also digitizing their offerings. Economic downturns may reduce willingness to pay for legal resources as businesses and individuals cut discretionary spending.
- Competitive Risks: Large established players like LegalZoom and Rocket Lawyer have significant brand recognition and marketing budgets. Free alternatives from government websites and non-profits provide basic legal information. Law firms are increasingly creating their own digital resource hubs for client acquisition. AI-driven legal tech startups with substantial venture funding could outpace Lawrina’s innovation cycles.
- Business Model Risks: The freemium model may create conversion challenges if the value differential between free and paid tiers isn’t compelling enough. Subscription fatigue among consumers might limit willingness to add another recurring payment. Balancing content quality (requiring legal expertise) with technical platform needs creates high operational costs. Scaling content across multiple jurisdictions requires significant investment in localized legal expertise.
These risks are particularly pronounced in the legal tech sector due to the inherently complex and jurisdiction-specific nature of legal information. Lawrina’s ability to maintain current, accurate legal content across multiple practice areas while continuously innovating its platform features will be crucial for mitigating these risks. Additionally, the platform must carefully balance accessibility for non-legal users while maintaining sufficient depth and accuracy to retain professional legal users – a challenging equilibrium that few competitors have successfully achieved.
7.2 Growth Opportunities
Despite facing significant challenges, Lawrina has several promising growth opportunities across different time horizons that could strengthen its market position and expand its user base.
- Short-term Opportunities: Expanding document template offerings to cover more specialized legal areas (intellectual property, immigration, healthcare compliance). Implementing AI-assisted document completion to improve user experience. Developing mobile application for on-the-go legal resource access. Creating tiered subscription models for different user segments (individuals, small businesses, legal professionals).
- Medium to Long-term Opportunities: International expansion to English-speaking markets beyond the US (UK, Canada, Australia). Integration with legal practice management systems used by law firms. Development of customized enterprise solutions for legal departments. Creation of continuing legal education (CLE) content for attorneys. Building community features to connect legal professionals with potential clients.
- Differentiation Opportunities: Developing industry-specific legal resource packages (e.g., for technology startups, healthcare providers, creative professionals). Creating interactive legal decision trees that guide users through complex legal scenarios. Offering real-time legal compliance monitoring for businesses. Implementing blockchain-based document verification for enhanced security and authenticity.
These opportunities align well with broader legal industry trends toward digitization, accessibility, and specialized expertise. By strategically pursuing these growth avenues, Lawrina can strengthen its competitive position while addressing unmet needs in the legal resources market. The most promising immediate opportunity appears to be expanding specialized content offerings while implementing AI-assisted features to enhance user experience and document completion – capabilities that would directly address current pain points while leveraging Lawrina’s existing content expertise and technological foundation. Medium-term focus on creating more robust connections between legal professionals and potential clients could establish Lawrina as not just a resource repository but an active marketplace and community, significantly increasing its value proposition and user retention.
7.3 SWOT Analysis
The following SWOT analysis systematically evaluates Lawrina’s internal strengths and weaknesses alongside external opportunities and threats to provide strategic insights.
Strengths
- Comprehensive legal document template library covering multiple practice areas
- User-friendly interface accessible to both legal professionals and laypeople
- Established credibility through expert-reviewed content
- Flexible freemium business model that attracts diverse user segments
Weaknesses
- Limited brand recognition compared to major legal resource competitors
- Resource constraints for rapidly expanding content across all jurisdictions
- Possible technical debt from early platform development choices
- Challenge of simultaneously serving professional and consumer legal markets
Opportunities
- Growing demand for accessible legal resources among underserved markets
- Increasing acceptance of digital legal solutions post-pandemic
- Potential partnerships with legal education providers and law schools
- Integration of emerging AI technologies for document analysis and creation
Threats
- Aggressive expansion of well-funded competitors like LegalZoom
- Regulatory changes affecting online legal service providers
- Potential market consolidation through acquisitions
- AI-driven disruption of traditional legal document creation processes
SWOT-Based Strategic Directions
- SO Strategy: Leverage content expertise to develop AI-enhanced, specialized legal resources that cater to specific industries or practice areas, thereby capitalizing on digital transformation trends while differentiating from generalist competitors.
- WO Strategy: Address brand recognition limitations by forming strategic partnerships with legal education providers, bar associations, and industry groups to expand reach while sharing content development costs.
- ST Strategy: Counter competitive threats by enhancing the human expertise component of the platform – offering more personalized guidance and expert validation that pure AI solutions cannot yet match.
- WT Strategy: Mitigate resource constraints and competitive pressure by focusing on specific underserved legal practice areas or industries rather than attempting to compete across all legal domains simultaneously.
8. Conclusions and Insights
8.1 Comprehensive Evaluation
Our analysis provides a comprehensive evaluation of Lawrina’s business model, market positioning, and growth potential in the legal resources marketplace.
- Business Model Sustainability: Lawrina’s freemium model with subscription tiers appears fundamentally sound for the legal resources market. The combination of free basic resources with premium specialized templates and tools creates an effective acquisition and conversion funnel. The recurring revenue from subscriptions provides predictable income, while the digital delivery model enables scalability without proportional cost increases. However, content development and maintenance costs represent a significant ongoing investment that must be carefully managed to maintain profitability.
- Market Competitiveness: Lawrina occupies a solid middle-market position in the legal resources space. While not commanding the brand recognition of market leaders like LegalZoom, its focus on both professional and consumer legal needs creates a distinct market position. The platform’s balance of accessibility and professional-grade resources differentiates it from purely consumer-focused alternatives. However, the platform faces intense competition from both established players and emerging AI-driven legal tech startups.
- Growth Potential: Lawrina demonstrates substantial growth potential, particularly in specialized practice areas and underserved market segments. The platform’s existing infrastructure provides a foundation for expansion into adjacent services and international markets. The growing acceptance of digital legal solutions post-pandemic creates favorable tailwinds. However, realizing this potential will require significant investment in content development, technological innovation, and market expansion initiatives.
Lawrina’s position at the intersection of professional and consumer legal markets gives it unique advantages but also creates challenges in resource allocation and messaging. The platform’s future success will largely depend on its ability to maintain the delicate balance between accessibility for non-legal users and sufficient depth for professionals, while strategically expanding its content library and feature set. The rapidly evolving legal tech landscape presents both opportunities and threats, requiring Lawrina to remain nimble in its product development and market approach. With proper execution and strategic focus, Lawrina has the potential to significantly strengthen its market position in the coming years, particularly by developing deeper expertise in select practice areas rather than attempting to match the breadth of larger competitors.
8.2 Key Insights
Our analysis of Lawrina reveals several important insights about its current position and future prospects in the legal resources market.
Key Strengths
- Dual-market approach serving both legal professionals and consumers creates unique positioning that most competitors have failed to successfully balance
- Comprehensive template library covering multiple practice areas provides immediate practical value and addresses specific user needs
- Expert-validated content establishes credibility in a field where accuracy and reliability are paramount
Key Challenges
- Maintaining content accuracy and currency across multiple jurisdictions requires significant ongoing investment
- Differentiating from both established competitors and emerging AI-driven alternatives in an increasingly crowded market
- Converting free users to paid subscribers in a market where users have access to basic legal information from free government and non-profit sources
Core Differentiation Elements
Lawrina’s most significant differentiation lies in its ability to bridge the gap between professional-grade legal resources and accessible consumer solutions. While most competitors focus predominantly on either legal professionals or consumers, Lawrina attempts to serve both audiences with appropriate depth and accessibility. This dual-market approach is challenging to execute but creates unique opportunities for cross-market network effects and differentiated positioning. By maintaining expert validation of content while ensuring user-friendly interfaces and clear explanations, Lawrina can potentially capture market share from both professional resource providers (by being more accessible) and consumer legal services (by offering greater depth and accuracy).
8.3 SaaS Scorecard
This quantitative assessment on a 1-5 scale evaluates Lawrina’s overall competitiveness across key success factors for SaaS businesses in the legal resources market.
| Assessment Criteria | Score (1-5) | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Product Capability | 4 | Strong document template library and resources, with good usability for both professional and consumer users. Room for improvement in AI-assisted features and document automation capabilities. |
| Market Fit | 4 | Well-positioned to address growing demand for accessible legal resources, particularly for small businesses and individuals. Successfully bridges professional and consumer needs. |
| Competitive Positioning | 3 | Solid middle-market position but faces intense competition from established players and well-funded startups. Lacks the brand recognition of market leaders. |
| Business Model | 4 | Freemium approach with subscription tiers is well-suited to the market. Good alignment between value delivery and monetization. Some challenges in conversion optimization. |
| Growth Potential | 4 | Significant opportunities for expansion in specialized practice areas, international markets, and adjacent services. Well-positioned to benefit from increasing digitization of legal services. |
| Total Score | 19/25 | Good – Strong fundamentals with clear opportunities for improvement |
With a total score of 19/25, Lawrina demonstrates strong overall competitiveness in the legal resources SaaS market. The platform scores particularly well in product capability, market fit, and business model alignment – core elements that provide a solid foundation for sustainable growth. Its relative weakness in competitive positioning reflects the challenging market environment rather than fundamental flaws in the platform itself. The strong growth potential score indicates significant opportunities for expansion if the company can execute effectively on its strategic initiatives. This scorecard suggests that Lawrina has established the fundamental elements required for success in the legal resources market, with its primary challenges revolving around differentiation and scale rather than core product-market fit or business model issues. With targeted improvements in competitive positioning and continued investment in product capabilities, Lawrina could strengthen its market position and realize its substantial growth potential.
9. Reference Sites
9.1 Analyzed Service
Lawrina’s official website and main service platform.
- Official Website: https://lawrina.org/ – A comprehensive legal resources platform offering templates, documents, and professional guidance for both legal practitioners and individuals navigating legal matters.
9.2 Competitive/Similar Services
Major services competing with or similar to Lawrina in the legal resources space.
- LegalZoom: https://www.legalzoom.com/ – Market leader in online legal services with extensive document templates and optional attorney support; more consumer-focused than Lawrina.
- Rocket Lawyer: https://www.rocketlawyer.com/ – Comprehensive legal document service with subscription model offering unlimited document creation and attorney consultations.
- Law Insider: https://www.lawinsider.com/ – Specialized in contract databases and clause analysis, more focused on legal professionals than general consumers.
- Practical Law (Thomson Reuters): https://legal.thomsonreuters.com/en/products/practical-law – Premium legal know-how service targeting law firms and legal departments with practice notes and templates.
9.3 Reference Resources
Useful resources for building or understanding similar SaaS businesses in the legal tech space.
- Legal Tech Hub: https://legaltechnologyhub.com/ – Comprehensive resource for understanding the legal technology landscape and various solution categories.
- American Bar Association Tech Resource Center: https://www.americanbar.org/groups/departments_offices/legal_technology_resources/ – Valuable insights on technology trends affecting the legal profession.
- DocuSign Developer Center: https://developers.docusign.com/ – API resources for implementing electronic signature capabilities, essential for modern legal document platforms.
- Clio’s Legal Trends Report: https://www.clio.com/resources/legal-trends/ – Annual report providing data-driven insights into the legal industry, useful for understanding market needs and opportunities.
10. New Service Ideas
LegalCraft AI
Overview
LegalCraft AI is an advanced legal document platform that combines industry-specific AI models with expert-curated templates to revolutionize contract creation and analysis. The platform goes beyond generic AI solutions by offering specialized models trained on specific industries (e.g., technology, healthcare, real estate) and practice areas. Users can draft customized agreements, analyze existing contracts for risks, and receive intelligent suggestions based on industry best practices. The system continuously learns from user interactions and legal expert input, creating increasingly sophisticated domain-specific intelligence that generic AI tools cannot match.
Who is the target customer?
▶ In-house legal teams at mid-size companies without extensive legal departments
▶ Solo practitioners and small law firms seeking to enhance efficiency
▶ Contract managers and procurement teams who regularly handle agreements
▶ Startups and small businesses that cannot afford dedicated legal counsel
What is the core value proposition?
Legal document creation and review historically requires significant expert time or carries risks when done without proper expertise. Generic templates often fail to address industry-specific nuances, while hiring attorneys for customization is expensive. LegalCraft AI bridges this gap by combining the efficiency of AI with industry-specific legal expertise. The platform reduces contract creation time by 70%, minimizes risk exposure from poorly drafted agreements, and provides context-aware recommendations that generic AI tools cannot deliver. Users gain access to sophisticated legal intelligence at a fraction of traditional legal costs while maintaining higher quality than generic template solutions.
How does the business model work?
• Industry Tier Subscriptions: Monthly/annual subscriptions to specific industry modules (Technology, Healthcare, Real Estate, etc.) with unlimited document creation and analysis within that domain
• Enterprise Plan: Custom-priced solution for larger organizations with API access, integration capabilities, and customization options
• Pay-per-Analysis: Credit-based system for users who need occasional deep analysis of complex third-party contracts
What makes this idea different?
Unlike general-purpose AI tools that lack legal context or template-based services with limited customization, LegalCraft AI delivers truly industry-specific legal intelligence. The platform combines specialized AI models trained exclusively on legal documents from specific sectors with continuous expert oversight to ensure accuracy. While competitors offer either generic AI capabilities or static templates, LegalCraft provides a dynamic system that evolves with industry standards and learns from user interactions. Additionally, the focus on specific industries creates network effects and allows for deeper expertise development compared to one-size-fits-all alternatives.
How can the business be implemented?
- Develop core AI analysis and drafting engine using transformer-based models trained on anonymized legal documents
- Partner with industry-specific legal experts to create and validate initial template libraries and training data
- Build industry-focused modules starting with 2-3 high-demand sectors (e.g., technology, real estate)
- Create intuitive interface with guided workflows and clause suggestion features
- Implement feedback loops for continuous model improvement and expert review processes
What are the potential challenges?
• Maintaining legal accuracy while scaling requires robust quality control and expert validation systems
• Privacy and confidentiality concerns with document processing require stringent security measures and clear data policies
• Regulatory considerations around unauthorized practice of law necessitate careful positioning as a tool rather than legal advice
LegalLens Compliance
Overview
LegalLens Compliance is a comprehensive regulatory monitoring and compliance management platform that helps businesses navigate the increasingly complex landscape of legal requirements. The service continuously monitors regulatory changes across multiple jurisdictions and industries, notifying businesses of relevant updates and translating legal requirements into actionable compliance tasks. Using AI and expert legal analysis, LegalLens interprets how regulatory changes impact specific business operations, assigns responsibility for compliance tasks to appropriate team members, tracks implementation, and maintains audit-ready compliance records. The platform bridges the gap between abstract legal requirements and practical business operations.
Who is the target customer?
▶ Compliance officers and legal teams at mid-size businesses
▶ Operations leaders in highly regulated industries (finance, healthcare, etc.)
▶ Risk management professionals responsible for legal compliance
▶ Business owners expanding into new jurisdictions or regulated activities
What is the core value proposition?
Businesses face increasing regulatory complexity with severe penalties for non-compliance, yet most lack resources to continuously monitor and interpret regulatory changes across all relevant jurisdictions. Traditional approaches either miss critical updates or require expensive legal counsel to interpret abstract regulations into practical business requirements. LegalLens solves this by providing automated regulatory monitoring combined with practical implementation guidance. The platform reduces compliance risk by ensuring no relevant regulatory changes are missed, translates legal jargon into actionable tasks, and creates accountability through workflow management. This dramatically reduces both the risk of non-compliance penalties and the operational costs of maintaining compliance programs.
How does the business model work?
• Industry-Specific Compliance Packages: Subscription tiers focused on specific regulatory domains (Data Privacy, Employment, Financial, Environmental, etc.)
• Jurisdiction Expansion Modules: Add-on packages for businesses operating in multiple states or countries
• Enterprise Compliance Solution: Customized platform with API integrations to existing business systems and tailored workflow automation
What makes this idea different?
Unlike traditional legal information services that simply aggregate regulatory updates or generic workflow tools lacking legal expertise, LegalLens provides end-to-end compliance management that connects regulatory monitoring directly to operational execution. The platform’s unique strength is translating abstract legal requirements into specific business tasks with clear ownership and accountability. While competitors focus either on information delivery or workflow management, LegalLens bridges both worlds. Additionally, the platform’s predictive capabilities can identify potential compliance issues before they materialize by analyzing patterns across similar businesses and regulatory enforcement trends.
How can the business be implemented?
- Build regulatory monitoring infrastructure with data feeds from government sources and regulatory bodies
- Develop AI-based classification system to identify industry-relevant regulatory changes
- Create compliance task library mapping common regulatory requirements to business actions
- Implement workflow management system with responsibility assignment and tracking
- Establish expert review process for validating AI-generated compliance interpretations
What are the potential challenges?
• Maintaining accuracy across multiple rapidly changing regulatory environments requires sophisticated monitoring systems
• Balancing automation with expert oversight to ensure regulatory interpretations are legally sound
• Integrating with diverse business systems for streamlined workflow implementation
DisputeResolver
Overview
DisputeResolver is an innovative platform that combines AI technology with human mediation expertise to provide accessible, affordable dispute resolution services. The platform helps businesses and individuals resolve conflicts without expensive litigation by offering structured negotiation frameworks, AI-assisted settlement recommendation engines, and on-demand access to certified mediators. Users can document disagreements, explore potential resolutions through guided processes, and receive data-driven insights about similar case outcomes. For more complex disputes, the platform facilitates virtual mediation sessions with qualified neutrals at a fraction of traditional legal costs. DisputeResolver makes professional conflict resolution accessible to those who typically cannot afford traditional legal services.
Who is the target customer?
▶ Small business owners facing contract or customer disputes
▶ Individuals with landlord-tenant, consumer, or small claims issues
▶ HR departments handling workplace conflicts
▶ Online marketplaces seeking to offer dispute resolution services
What is the core value proposition?
The current justice system makes dispute resolution prohibitively expensive and time-consuming for most small businesses and individuals. Legal fees often exceed the value of the dispute, court backlogs extend resolution timelines for years, and adversarial processes damage ongoing relationships. DisputeResolver addresses these problems by providing structured, technology-assisted conflict resolution at accessible price points. The platform reduces resolution time from months to days, decreases costs by 80% compared to traditional legal processes, preserves relationships through collaborative approaches, and provides clear documentation of agreements reached. This democratizes access to effective conflict resolution for disputes that would otherwise remain unresolved or result in disproportionate legal expenses.
How does the business model work?
• Self-Service Tier: Pay-per-case access to AI-assisted negotiation tools and settlement frameworks
• Mediation Marketplace: Commission-based model connecting users with certified mediators for virtual sessions
• Enterprise Solution: Subscription service for businesses handling multiple disputes (e.g., HR departments, customer service teams)
• API Integration: White-label solutions for online marketplaces and platforms to offer dispute resolution to their users
What makes this idea different?
Unlike traditional legal services that are prohibitively expensive or simplistic DIY legal forms that lack guidance, DisputeResolver provides a hybrid approach combining technology and human expertise. The platform’s unique value comes from its data-driven settlement recommendation engine that analyzes thousands of similar disputes to suggest realistic resolution parameters. While legal tech typically focuses on document preparation or lawyer matching, DisputeResolver focuses specifically on the neglected middle ground of facilitated negotiation and mediation. The platform also uniquely emphasizes relationship preservation rather than just dispute termination, making it especially valuable for ongoing business relationships.
How can the business be implemented?
- Develop structured negotiation frameworks for common dispute types based on mediation best practices
- Build case analysis engine to compare current disputes with historical data and outcome patterns
- Create secure virtual mediation environments with document sharing and agreement drafting capabilities
- Establish certification process and marketplace for professional mediators
- Implement API and white-label solutions for integration with existing platforms
What are the potential challenges?
• Navigating regulatory considerations around unauthorized practice of law in different jurisdictions
• Building sufficient case data for accurate settlement recommendations while maintaining privacy
• Establishing credibility in a field traditionally dominated by legal professionals
Disclaimer & Notice
- Information Validity: This report is based on publicly available information at the time of analysis. Please note that some information may become outdated or inaccurate over time due to changes in the service, market conditions, or business model.
- Data Sources & Analysis Scope: The content of this report is prepared solely from publicly accessible sources, including official websites, press releases, blogs, user reviews, and industry reports. No confidential or internal data from the company has been used. In some cases, general characteristics of the SaaS industry may have been applied to supplement missing information.
- No Investment or Business Solicitation: This report is not intended to solicit investment, business participation, or any commercial transaction. It is prepared exclusively for informational and educational purposes to help prospective entrepreneurs, early-stage founders, and startup practitioners understand the SaaS industry and business models.
- Accuracy & Completeness: While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information, there is no guarantee that all information is complete, correct, or up to date. The authors disclaim any liability for any direct or indirect loss arising from the use of this report.
- Third-Party Rights: All trademarks, service marks, logos, and brand names mentioned in this report belong to their respective owners. This report is intended solely for informational purposes and does not infringe upon any third-party rights.
- Restrictions on Redistribution: Unauthorized commercial use, reproduction, or redistribution of this report without prior written consent is prohibited. This report is intended for personal reference and educational purposes only.
- Subjectivity of Analysis: The analysis and evaluations presented in this report may include subjective interpretations based on the available information and commonly used SaaS business analysis frameworks. Readers should treat this report as a reference only and conduct their own additional research and professional consultation when making business or investment decisions.

No comment yet, add your voice below!